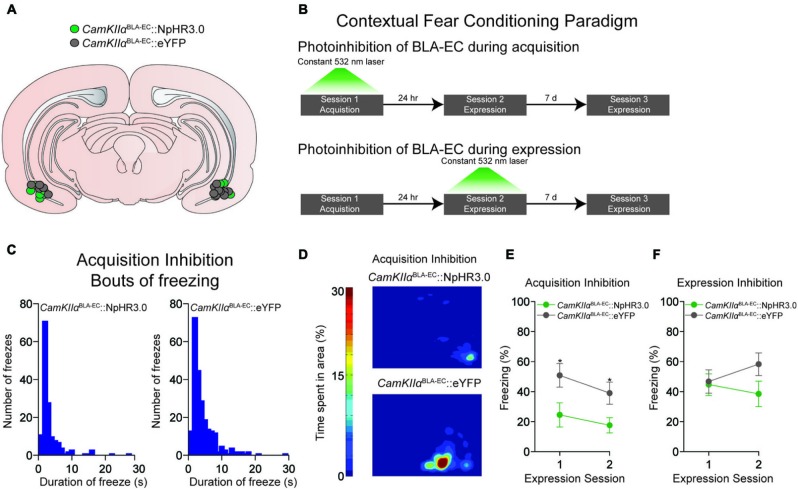
Figure 2.
Photoinhibition of the glutamatergic pathway from the BLA to the EC during contextual fear conditioning. (A) Schematic diagram showing optical fiber placement for CamKIIαBLA-EC::NpHR3.0 (n = 17 mice) and CamKIIαBLA-EC::eYFP (n = 16 mice) in the EC for all behavioral experiments (D = dorsal; V = ventral; M = medial; L = lateral). (B) Schematic illustrating the different contextual dear conditioning paradigms employed. (C) Histogram depicting the number of freezes during the first expression session in the CamKIIαBLA-EC::NpHR3.0 group (left) and CamKIIαBLA-EC::eYFP (right) after laser inhibition during the acquisition session. Length of freezes were cut off at 30 s, although there were a few bouts (1 in the CamKIIαBLA-EC::NpHR3.0 group; 3 in the CamKIIαBLA-EC::eYFP group) that lasted longer than our 30 s cutoff time epoch. (D) Representative heat maps displaying average time spent in the context during the first expression session after laser inhibition during the acquisition session from CamKIIαBLA-EC::NpHR3.0 (top) and CamKIIαBLA-EC::eYFP (bottom) mice. (E) Average freezing (%) of CamKIIαBLA-EC::NpHR3.0 (n = 8 mice) and CamKIIαBLA-EC::eYFP (n = 8 mice) during the two expression sessions after laser stimulation during the acquisition session. CamKIIαBLA-EC::NpHR3.0 mice spent significantly less time frozen during both expression sessions compared to CamKIIαBLA-EC::eYFP. (F) Average freezing (%) of CamKIIαBLA-EC::NpHR3.0 (n = 9 mice) and CamKIIαBLA-EC::eYFP (n = 8 mice) during two expression sessions after laser stimulation during the 1st expression session, showing no differences between the groups. All values for all figures represent mean ± s.e.m. * P < 0.05.