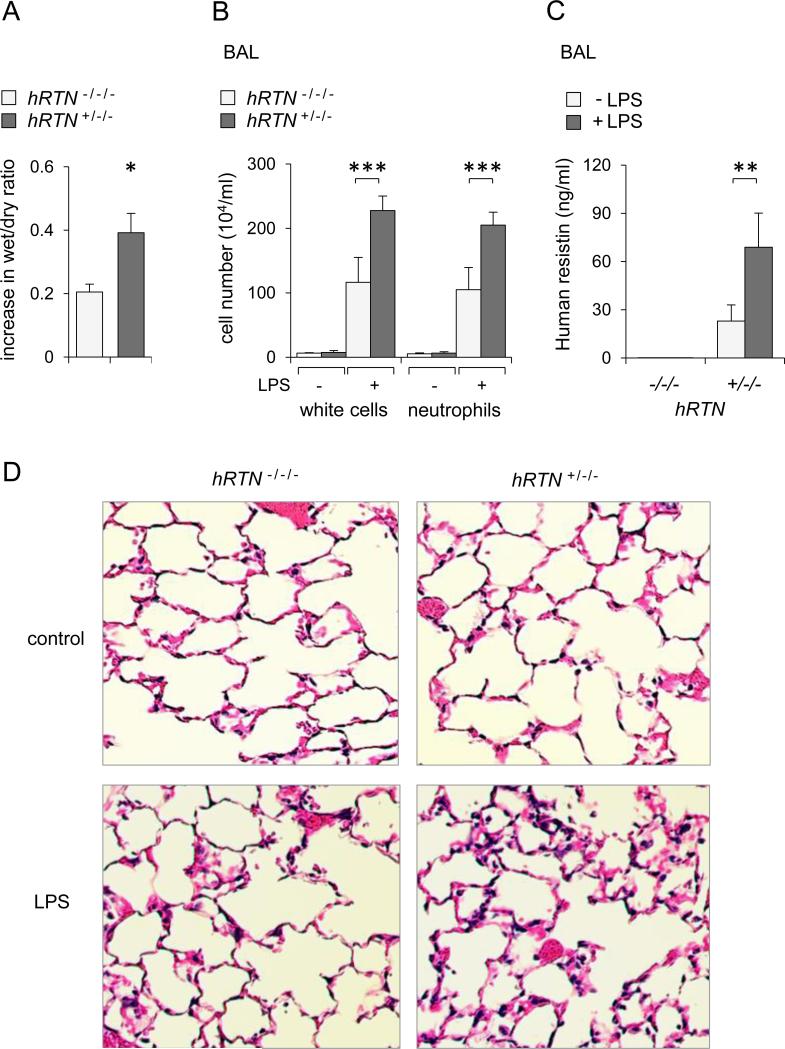
Figure 4. Human resistin increases severity of LPS-induced acute lung injury.
hRTN+/−/− or control RTN−/−/− mice were subjected to intratracheal application of LPS (0 or 2 mg/kg) for 24 hours. Panel (A) shows lung wet-to-dry ratios measured 24 hours after LPS administration. Fold increase above values present in mice receiving saline alone are shown (Means ± SEM, n = 4-5, * P < 0.05). Panel (B) shows numbers of total white cells and neutrophils in BAL fluid from saline (-LPS) or LPS (+LPS) treated mice (Means ± SD, n = 3-6, *** P < 0.001). (C) Human resistin was measured in BALs of hRTN+/−/− or hRTN+/−/− mice treated with saline (-LPS) or LPS (+LPS) 24 hours previously (Means ± SD, n = 5, ** P < 0.01). Panel (D) shows representative H&E staining of lung sections obtained from control (saline) or LPS-treated hRTN+/−/− or RTN−/−/− mice.