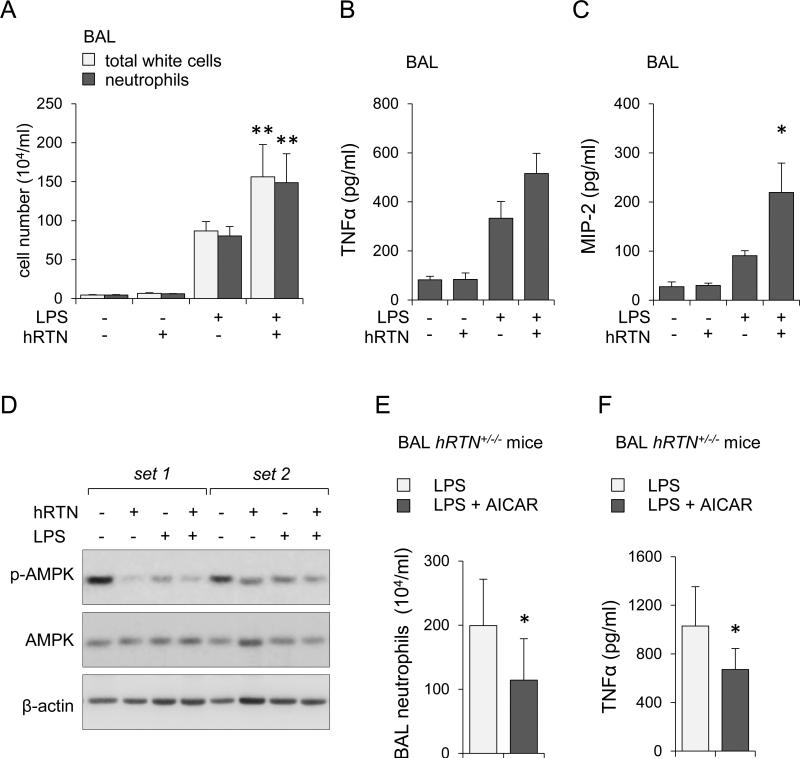
Figure 6. Co-administration of human resistin and LPS increases the severity of ALI.
(A, B, C, and D) wild type mice were subjected to intratracheal (i.t.) instillation of purified human resistin (0.5 mg/kg), LPS (2 mg/kg), or combined administration of human resistin and LPS, and then BALs obtained 24 hours later. Panels (A ) and (B) show numbers of total white cells, neutrophils and levels of TNF-α and MIP-2 in BAL fluid (Means ± SD, n = 4, * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01). (D) Representative Western blots showing phospho-Ser172 AMPK, total AMPK, and β-actin in lung homogenates. (E and F) hRTN+/−/− mice were treated with saline or AICAR (i.p., 500 mg/kg) 4 hours prior to intratracheal instillation of LPS (2 mg/kg). Numbers of neutrophils (E) and levels of TNF-α (F) in BAL fluids were measured 24 hours after LPS injection (Means ± SD, n = 4, * P < 0.05).