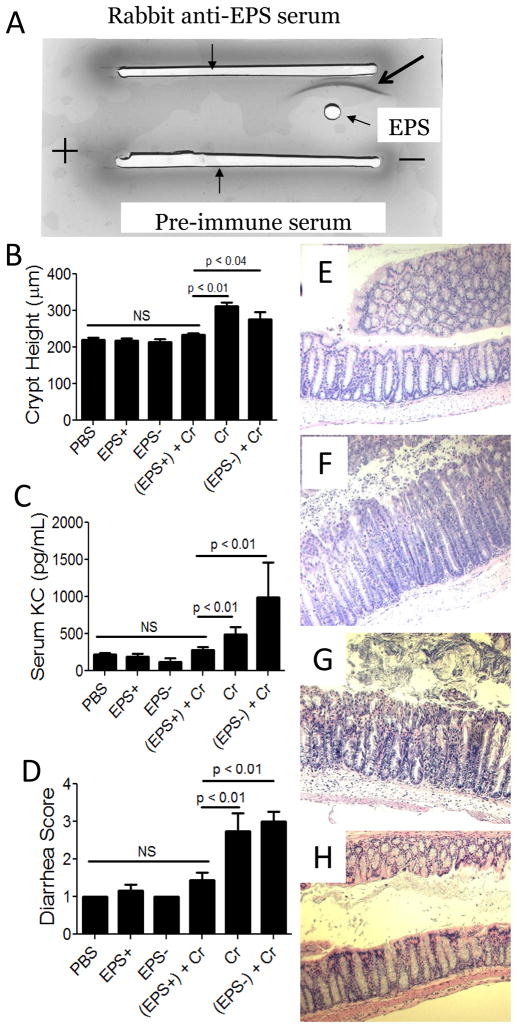
Figure 2. Assessment of the B. subtilis exopolysaccharides on C. rodentium-associated disease 10 days post-infection dpi of wt mice.
A) Immunoelectrophoresis analysis of purified EPS (arrow points to precipitation arc). B) Average colonic crypt heights from each treatment group. Serum KC levels (C), and evidence of diarrhea (D) were also used as disease markers. Results are averages from at least three independent experiments; a total of 5–12 mice were assessed for each group. PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; EPS+, exopolysaccharide from B. subtilis strain DS991; EPS−, material from B. subtilis strain DS5187; Cr, C. rodentium. Representative images of H&E stained colons from wildtype mice (100X). Images are representative of mice that received EPS from DS991 prior to C. rodentium infection (E), or material from the non-EPS producing strain DS5187 prior to pathogen infection (F). Representative images from myeloid MyD88 KO mice (G) and epithelial MyD88 KO mice (H) treated with EPS prior to infection with C. rodentium.