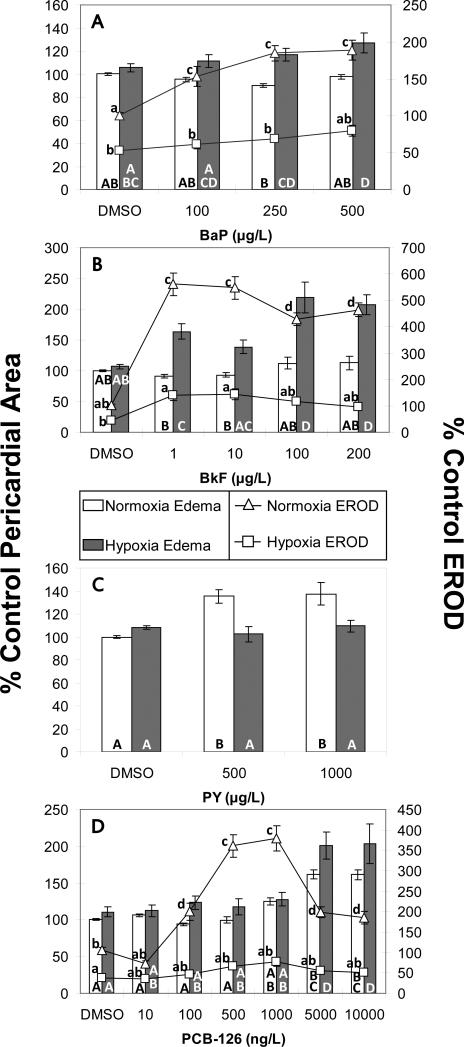
Fig. 4.
The effects of CYP1A-mo on zebrafish larvae exposed to BkF or PY and hypoxia or normoxia. BkF (A, B, C) (A) BkF-induced EROD activity was decreased by the CYP1A-mo and by hypoxia and the effect of BkF on EROD activity under hypoxia was eliminated by CYP1A-mo (BkF*oxygen*mo interaction: p<0.002). (B) Hypoxia and the CYP1A-mo interacted with BkF to induce pericardial edema at otherwise non-toxic concentrations (BkF*oxygen*mo interaction: p<0.004). (C) Hypoxia and CYP1A-mo interacted with BkF to induce mortality at otherwise non-lethal concentrations (BkF*oxygen*mo interaction: p<0.03). PY (D) 1000 μg/L PY induced pericardial edema under normoxic conditions; concurrent treatment with hypoxia or CYP1A-mo prevented this effect (PY*oxygen*mo interaction: p<0.04). NI=Non-injected. Treatments that do not share a letter are significantly different from one another in pairwise comparisons (p<0.05). Error bars are +/- standard error