Fig. 4.
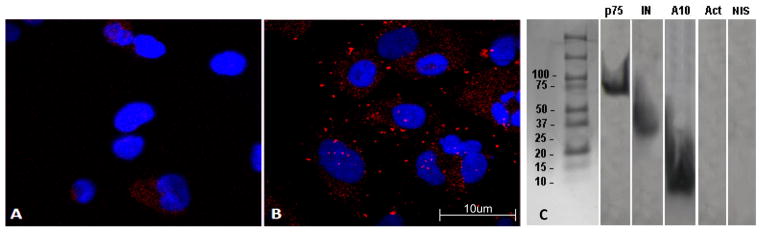
Colocalization and coimmunoprecipitation of the ADAM10 ICD and HIV-1 IN. U373 cells were co-cultured with the HIV-producing cell line, U1/HIV-1. Cells were stained with anti-IN and anti-ADAM10 ICD primary antibodies, followed by PLA secondary antibodies, and then fixed and imaged for immunofluorescence. Representative experiments are shown. (A) PLA results using an isotype-matched negative control anti-biotin antibody as the primary antibody. (B) Colocalization between the ADAM10 ICD and HIV-1 IN as revealed by PLA with punctate patterns of red fluorescence. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI for contrast. (C) U373 cells were co-cultured for 6 h with an HIV-1 producing cell line, U1/HIV-1. Subsequently, cells were harvested and cytoplasmic fractions were collected. Co-immunoprecipitation was performed using an anti-IN mAb. Precipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a poly-vinyl membrane, and analyzed in Western blots. The membranes were cut into strips and probed with the indicated monoclonal antibodies. p75/LEDGF and HIV-1 IN were used as positive controls to confirm that whole PICs were precipitated. Actin and non-immune serum (NIS) were used as negative controls for non-specific precipitation of cellular proteins.
