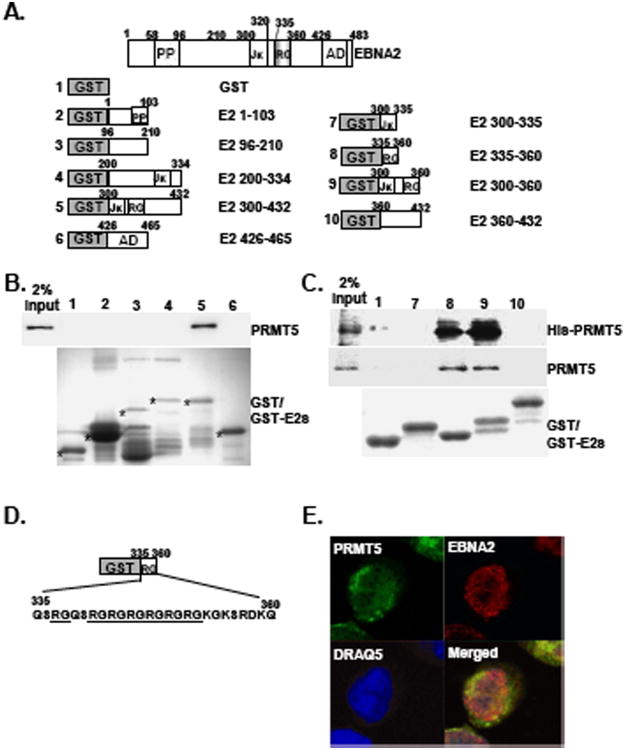
Fig. 1.
The EBNA2 RG repeat domain is the binding site for PRMT5 Schematic depiction of the GST-EBNA2 fusion proteins (GST-E2s). The amounts of the GST or GST-E2 fusion proteins were quantitated by coomassie blue staining following SDS-PAGE analysis. Each protein is marked with an individual asterisk (A). GST or GST-E2 fusion proteins were used as protein baits to pull down cell lysates from IB4 LCL (B) or the his-PRMT5 recombinant protein (C). The amount of endogenous PRMT5 or his-PRMT5 that was pulled down was determined by immunoblot analysis. Two percent input of PRMT5 or his-PRMT5 is shown. The coding sequences of the EBNA2 RG domain are shown (D). The immunofluorescence (IF) analysis was carried out using antibodies for EBNA2 (PE2) and PRMT5 (C-20) followed by counterstaining with a goat anti-mouse antibody conjugated to Rodamin (Red) or a donkey anti-goat antibody conjugated to FITC (Green). Confocal images for EBNA2 (Red) and PRMT5 (Green) from IB4 cells are shown. Nuclei were counterstained with DRAQ5 (Blue)(E).