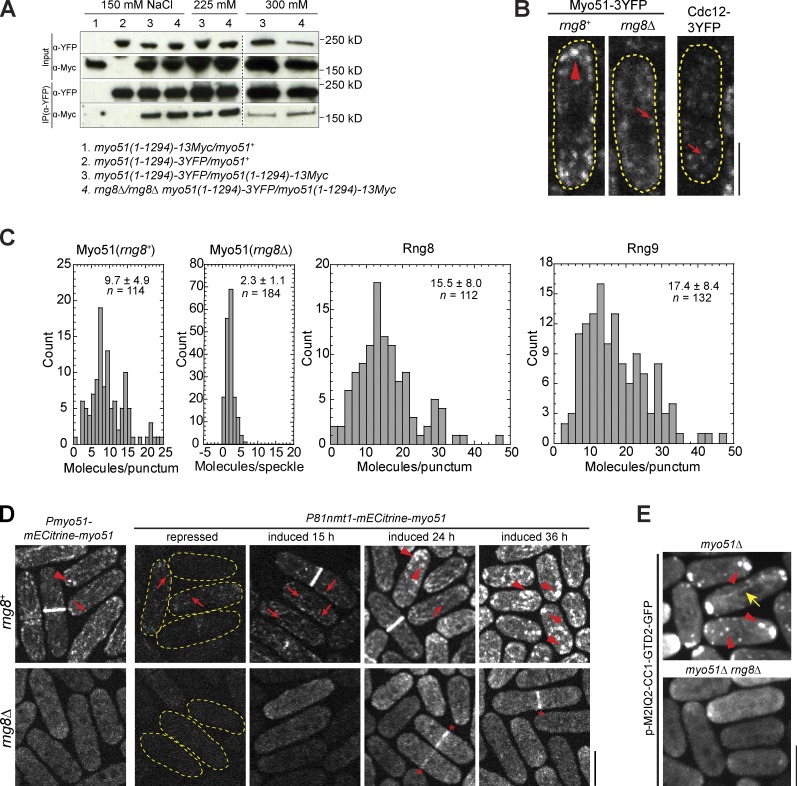
Figure 7.
The Rng8–Rng9 complex promotes Myo51 clustering. (A) Myo51 self-interaction does not depend on Rng8 or Rng9 in coIP assays of cell extracts from diploid cells at different salt concentrations. Both copies of Myo51 are the truncation without the GTD domain. The broken lines indicate that intervening lanes have been spliced out. (B) Single focal plan showing Cdc12 speckles, Myo51 speckles, and Myo51 puncta imaged at the same settings. Examples of brighter puncta and dimmer speckles are marked by an arrowhead and arrows, respectively. Cell boundaries are indicated by broken lines. (C) Histograms showing the molecule numbers in Myo51 puncta (rng8+) and speckles (rng8Δ), and in Rng8 and Rng9 puncta with mean and SD indicated. The intensities were compared with those of Cdc12 speckles (see Materials and methods). (D) Myo51 punctum formation depends on Rng8. The arrowheads, arrows, and asterisks indicate the puncta, speckles, and the contractile ring, respectively. (E) Punctum formation of the Myo51-Myo52 chimera M2IQ2-CC1-GTD2 depends on Rng8. The arrowheads and arrow indicate the puncta and a cable, respectively. Bars, 5 µm.