Figure 1. Vertebrate Eph receptor structure and signaling.
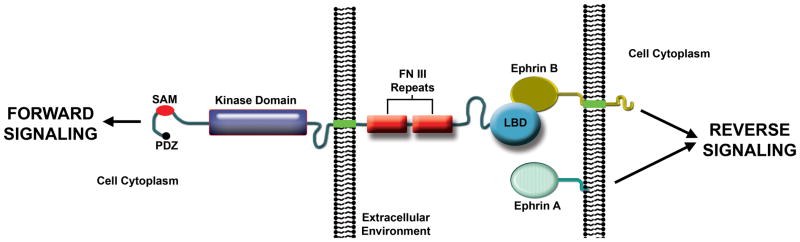
Ephrin-induced EphR clustering, autophosphorylation, and association of EphR intracellular domains with signaling effectors triggers “forward” signaling. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho family GTPases couple forward signals to the actin cytoskeleton. The transmembrane domain-containing B-type ephrins transmit “reverse” signals, whereby the EphR extracellular domain functions as a ligand. GPI-linked A-type ephrins are thought to transmit reverse signals, but the mechanism is not well understood (Arvanitis and Davy, 2008: PMID18281458; Pasquale, 2008: PMID18394988; Pitulescu and Adams, 2010: PMID21078817). LBD, ligand binding domain; FN III, fibronectin type III; SAM, sterile alpha motif; PDZ, post synaptic density protein/Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor/zonula occludens-1 protein domain binding.
