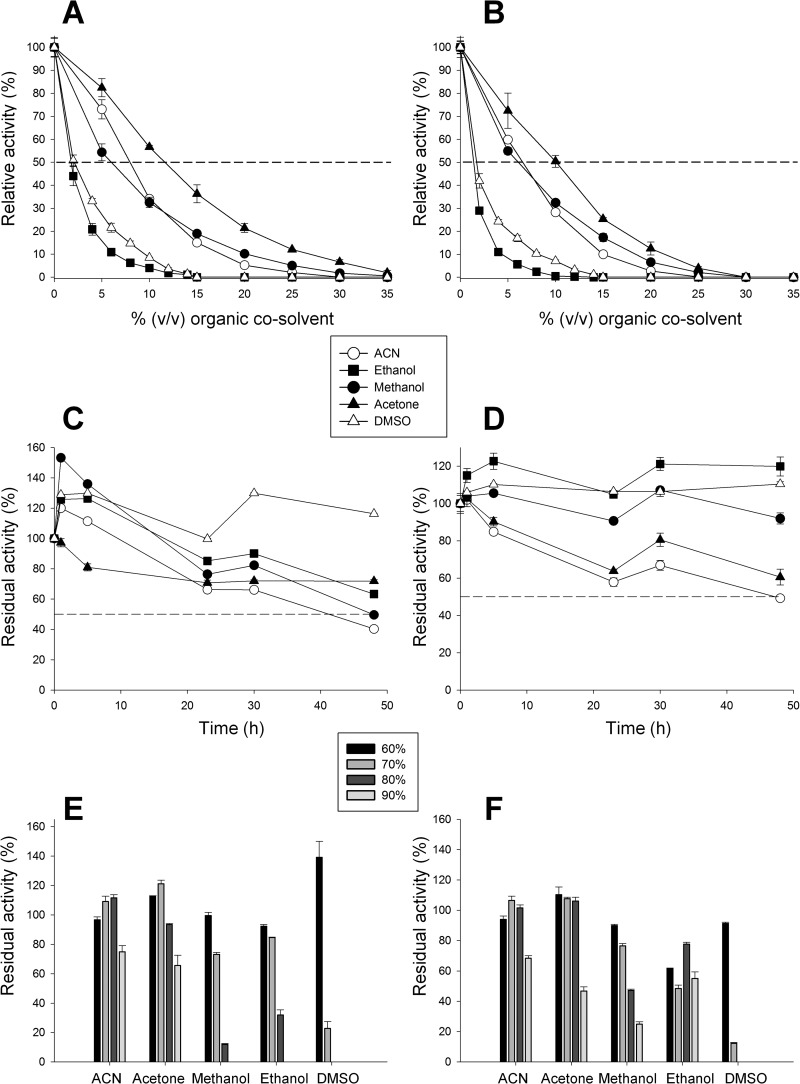
FIG 4.
Activity and stability in organic cosolvents. (A and B) The relative activities of wtUPO1 (A) and the PaDa-I mutant (B) in organic cosolvents were assessed with 2 mM H2O2 and 0.3 mM ABTS in 100 mM sodium phosphate/citrate buffer (pH 4.4) containing the corresponding concentration of cosolvent. (C and D) The stabilities of wtUPO1 (C) and the PaDa-I mutant (D) after incubation for 48 h in 50% organic cosolvents were assessed by incubating enzyme samples in 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing 50% (vol/vol) organic cosolvent in screw-cap vials. After 48 h, aliquots were removed and analyzed in an activity assay with 2 mM H2O2 and 0.3 mM ABTS in 100 mM sodium phosphate/citrate buffer (pH 4.4). (E and F) The stabilities of wtUPO1 (E) and the PaDa-I mutant (F) at high concentrations of organic cosolvents were assessed after 5 h of incubation in increasing concentrations of cosolvents and incubating enzyme samples at 20°C in 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing increasing concentrations (vol/vol) of organic cosolvent (60 to 90%). After 5 h, aliquots were removed and analyzed in the activity assay, as described for panels C and D. Residual activities were expressed as percentages of the original activity at the corresponding concentration of organic cosolvent. The error bars indicate standard deviations.