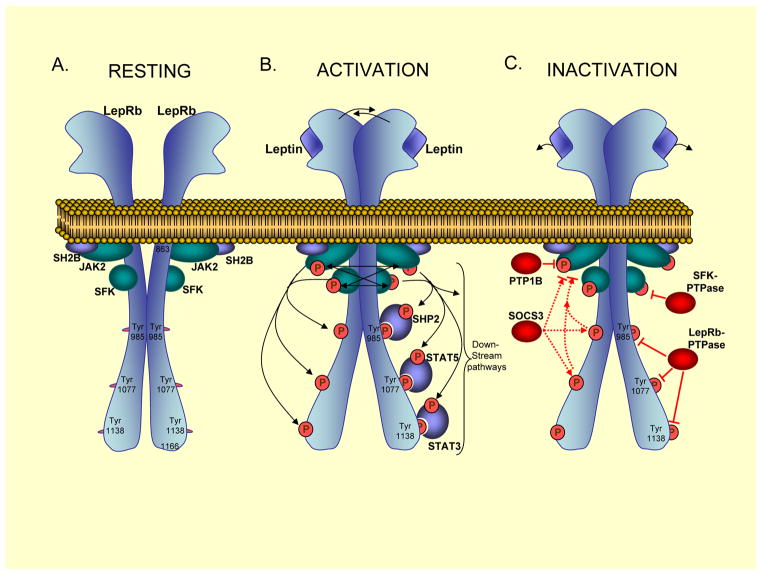
Figure 1. Neuronal Leptin Receptor Activation and Inactivation.
A. In the resting state, the long form leptin receptor (LepRb) exists as a homodimer at the plasma membrane153. The tyrosine kinases Janus Kinase (JAK2) and Src-Family-Kinases (SFKs), and the JAK2-binding protein SH2B, are constitutively associated with membrane-proximal regions of LepRb154,155. B. Upon ligand (leptin) binding to LepRb (1:1 stoichiometry156), the two receptor subunits undergo a conformational change resulting in transphosphorylation and transactivation of JAK2 and SFKs proteins157,158. SH2B enhances JAK2 enzymatic activity159. Activated JAK2 and possibly SFK enzymes, then phosphorylate LepRb tyrosine (Tyr) residues58. Three cytoplasmic Tyr residues of the murine LepRb acts as binding sites for SH2-domain containing proteins. Specifically, SHP2 principally binds to pY985, STAT5 to pY1077 and STAT3 to pY1338160,161. LepRb-bound SHP2, STAT3 and STAT5 proteins then become phosphorylated by JAK2 and SFKs. Additional downstream signalling proteins and pathways include PI3K-Akt; GRB2-Erk1/258,160,162; p90RSK58; p70RSK and ribosomal S6 proteins; and the forkhead box-containing protein O1 (FoxO1) 163,164. These enzymes and pathways ultimately exert regulation of cellular processes, including transcriptional control (socs3165,166, pomc167,168, cFos58, carboxypeptidase E (cpe)169, as well as agrp and npy 168), translational control170–172, and neuronal activity and firing109,173. C. LepRb is inactivated at proximal steps by PTP1B/PTPN1, a tyrosine phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates JAK276. Furthermore, SOCS3 acts to inhibit JAK2 activity by binding directly to JAK2 or indirectly by first binding to Tyr985 or Tyr 1077 of LepRb68,80,161. Finally, yet unidentified protein tyrosine phosphatases are predicted to directly dephosphorylate LepRb and SFKs.