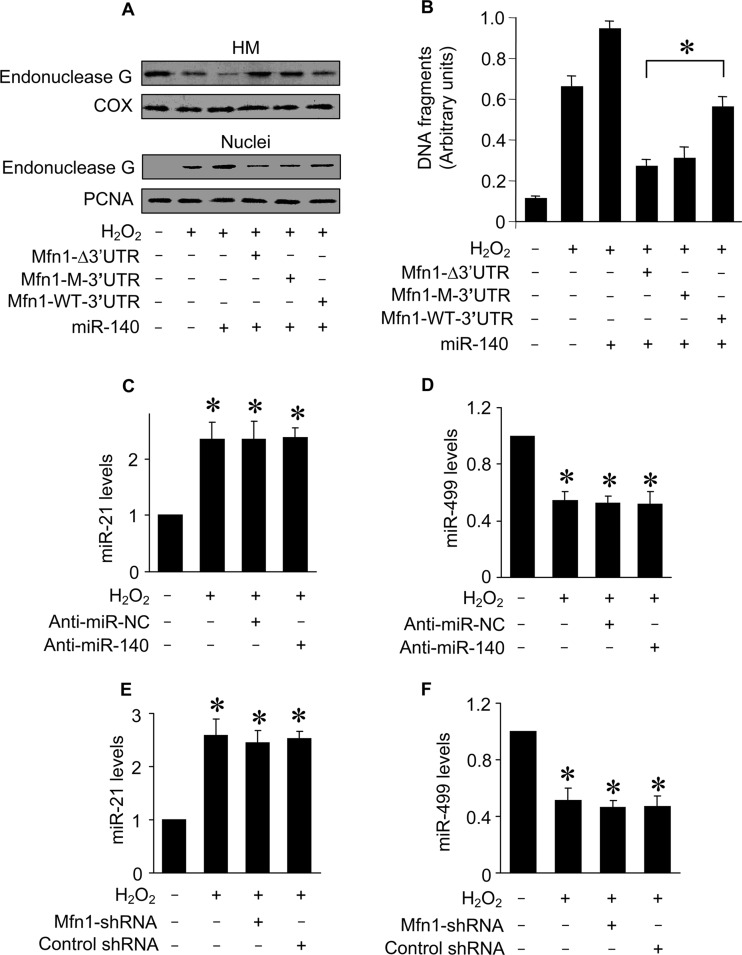
FIG 8.
miR-140 controls the downstream target of Mfn1. (A) Immunoblots of endonuclease G proteins in mitochondrion-enriched heavy membranes (HM) and nuclear fractions from cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes were infected with adenoviral Mfn1 whose mRNA lacked the 3′ UTR (Mfn1-Δ3′UTR), had the wild-type 3′ UTR (Mfn1-WT-3′UTR), or had the mutated 3′ UTR (Mfn1-M-3′UTR), along with adenoviral miR-140, and then exposed to H2O2. Cytochrome oxidase subunit V (COX) served as a mitochondrial marker. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) served as a nuclear marker. (B) DNA fragmentation in cardiomyocytes treated as described for panel A. Twelve hours after treatment, DNA fragments were analyzed by the Cell Death Detection ELISA kit, which specifically monitors histone-associated DNA fragments. *, P < 0.05. (C to F) Quantification of miR-21 and miR-499 levels by qRT-PCR. Cardiomyocytes were transfected with anti-miR-140 or anti-miR-NC (C and D) or infected with lentiviral particles expressing small hairpin RNA (shRNA) for Mfn1 or lentiviral control shRNA (E and F) and treated with H2O2. *, P < 0.05 versus the control. Data are expressed as means ± standard errors of the means of three independent experiments.