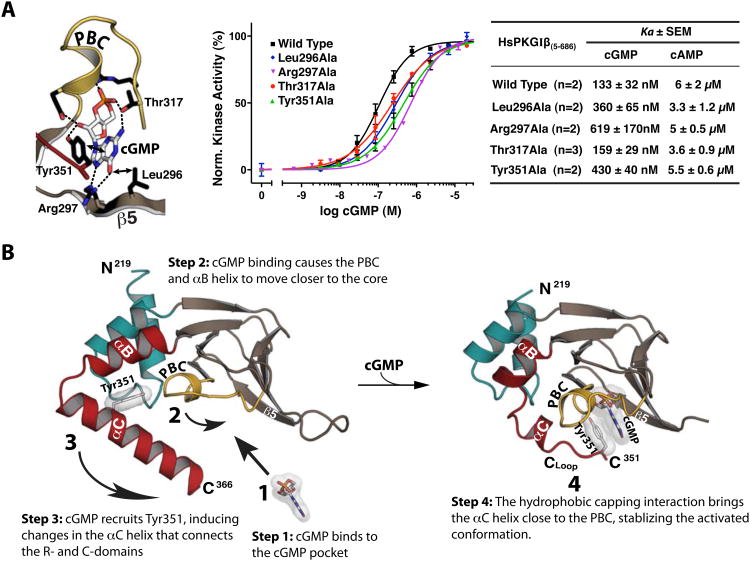
Figure 4. Role of CNB-B in activation and stepwise model for cGMP binding.
(A) Role of cGMP contact residues in kinase activation. Ka values were measured using a microfluidic mobility shift assay, and error bars denote standard error of measurement. (B) Stepwise model for cGMP binding and kinase activation. (1) cGMP binds to the pocket, interacting with the PBC and the β5 strand. (2) This interaction causes the PBC to tilt towards the core of CNB-B, causing the αB and αC helices to compact against the binding pocket. (3) The capping of cGMP by Tyr351. (4) The capping interaction stabilizes the activated conformation of CNB-B, dislodging the C-domain and activating the enzyme.