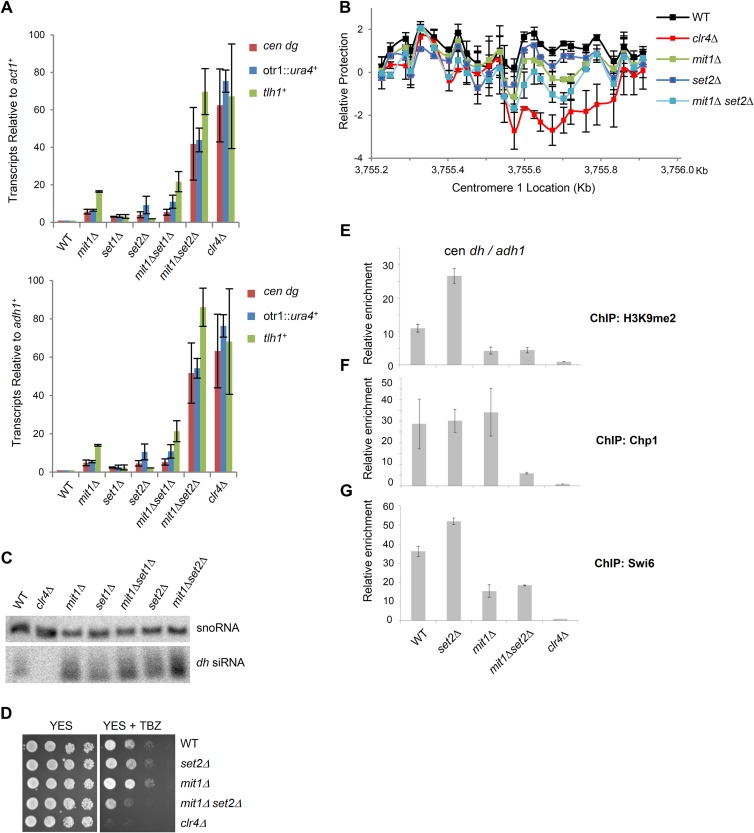
FIG 6.
Mit1 and Set2 synergize to silence heterochromatin transcripts. (A) Mit1 and Set2 cooperate to silence heterochromatin. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of transcripts from a centromeric transgene (otr1::ura4+), centromeric repeats (cen dh), and subtelomeres (tlh1+) in cDNA prepared from the indicated strain backgrounds. Transcript levels were normalized to act1+ transcripts (top) or adh1+ (bottom) and to transcripts in WT cells. Error bars represent SEM (n = 2). (B) In vivo nucleosome scanning of a centromeric dh sequence. Nucleosome scanning experiment comparing the relative protection of part of the dh centromeric repeat from digestion by micrococcal nuclease in wild-type, mit1Δ, set2Δ, mit1Δset2Δ, and clr4Δ backgrounds. Mononucleosomal DNA was analyzed by Q-PCR, normalized to amplification within adh1+, and compared to that of the wild type. Data are plotted on a log2 scale. Error bars represent SEM (n = 2). (C) Monitoring of RNAi. Northern blot of purified small RNA using probes corresponding to cen dh sequences and snoR69 for a loading control. (D) Thiabendazole sensitivity plating assay. Serial dilution assay of wild-type and mutant strains plated on YES medium or YES medium containing 15 μg/ml TBZ. Plates were incubated at 25°C. (E to G) ChIP analysis for strains lacking Mit1 and Set2. Immunoprecipitated and input chromatin was analyzed by Q-PCR for relative enrichment of centromeric dh sequence relative to adh1+ in immunoprecipitated chromatin with anti-H3K9me2 (E), anti-Chp1 (F), or anti-Swi6 (G). ChIPs are normalized to a clr4Δ strain. Error bars represent SEM (n = 2).