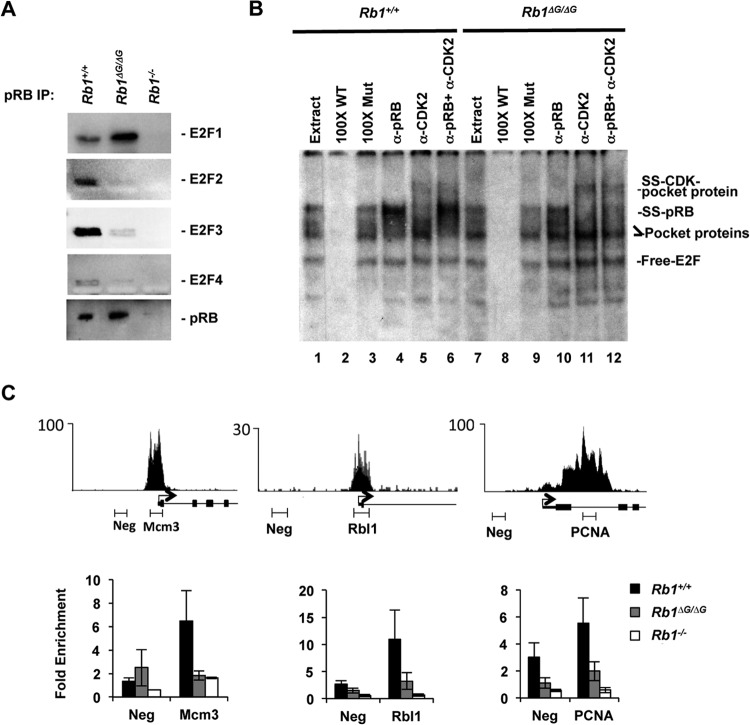
FIG 4.
Loss of ΔG-pRB binding at E2F-responsive promoters. MEFs were induced to exit the cell cycle by serum withdrawal, and pRB's interaction with E2Fs was investigated. (A) Anti-pRB antibodies were used to precipitate pRB, and associated E2F transcription factors were detected by Western blotting. (B) EMSAs were performed to compare the abundance of all pRB-E2F-containing complexes in Rb1+/+ and Rb1ΔG/ΔG nuclear extracts. The migration positions of free E2F, E2Fs bound to RB family proteins (labeled as pocket protein), antibody-supershifted pRB-E2F complexes (SS-pRB), and antibody-supershifted complexes containing p107/p130–E2F-cyclin-CDK (SS-CDK-pocket protein) are all indicated to the right. Cold competitor probes (100× WT and 100× Mut), as well as the antibodies used to shift complexes, are listed on top. (C) Sequence read peaks from ChIP sequence analysis of human pRB are shown for Mcm3, Rbl1, and Pcna on top. The locations of negative-control and proximal promoter PCR amplicons used in this study are shown along with the transcriptional start site and exons. ChIP quantitative PCR analysis was undertaken for pRB at the indicated promoters. All ChIP enrichment values are scaled relative to a neutral genome location, the GAPDH promoter. Error bars indicate the standard errors.