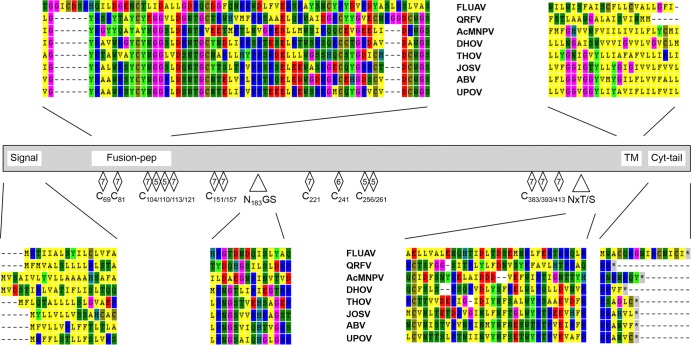
FIG 4.
Schematic of glycoprotein alignment including the tick-borne orthomyxoviruses Upolu virus (UPOV), Aransas Bay virus (ABV), Jos virus (JOSV), Thogoto virus (THOV), Dhori virus (DHOV), and Quaranfil virus (QRFV) as well as influenza A virus (FLUAV) and the insect Autographa californica multicapsid polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV), showing the signal peptide (Signal); motifs of a potential fusion peptide cleavage site proposed for THOV (Fusion-pep); cysteine (C) residues conserved in all orthomyxoviruses or in the tick-borne orthomyxoviruses and AcMNPV  , in tick-borne viruses and AcMNPV except DHOV
, in tick-borne viruses and AcMNPV except DHOV  , or in thogoto- and dhoriviruses or in thogotoviruses and AcMNPV
, or in thogoto- and dhoriviruses or in thogotoviruses and AcMNPV  ; conserved glycosylation sites surrounding position 183 (N183GS/N183GT; N197VT in AcMNPV) and position 415/428 (NxT/S, including N415/412/410XT/S in UPOV, ABV, and JOSV; N428/427/423/416XT/S in UPOV, ABV, JOSV, and THOV; N378NT in THOV; N396HS in DHOV; N422VS in QRFV; and N384NS/N426TT in AcMNPV); the trans-membrane anchor (TM); and amino acids of the cytoplasmic tail region (Cyt-tail).
; conserved glycosylation sites surrounding position 183 (N183GS/N183GT; N197VT in AcMNPV) and position 415/428 (NxT/S, including N415/412/410XT/S in UPOV, ABV, and JOSV; N428/427/423/416XT/S in UPOV, ABV, JOSV, and THOV; N378NT in THOV; N396HS in DHOV; N422VS in QRFV; and N384NS/N426TT in AcMNPV); the trans-membrane anchor (TM); and amino acids of the cytoplasmic tail region (Cyt-tail).