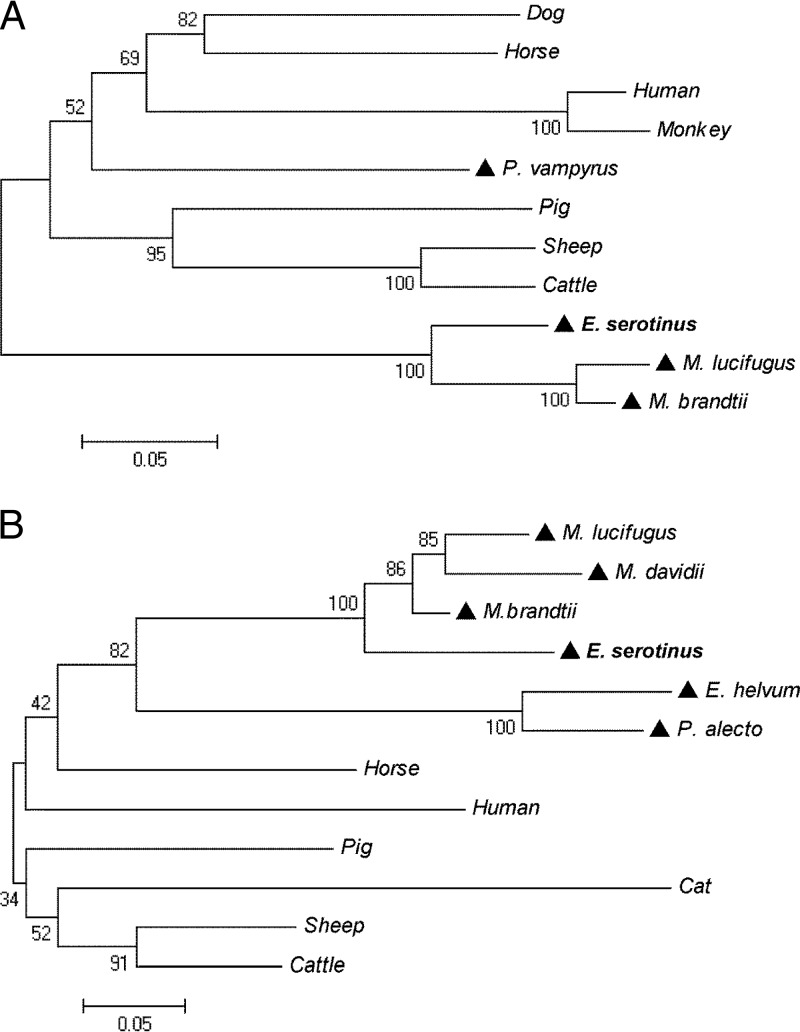
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of IFN-κ (A) and IFN-ω (B) protein sequences by neighbor-joining method with bootstrap value at n = 1,000. (A) Protein sequences used for IFN-κ: dog, Canis lupus familiaris (XP_003639432); human, Homo sapiens (NP_064509); horse, Equus caballus (XP_001497233); pig, Sus scrofa (NP_001158329); monkey, Nomascus leucogenys (XP_003281871); sheep, Ovis aries (XP_004004472); cattle, Bos Taurus (NP_001193352); and bats, P. vampyrus (ADK60922), M. brandtii (EPQ20610), M. lucifugus (GL430113:491398:492675:1), and E. serotinus (KF758763). (B) Protein sequences used for IFN-ω: human, H. sapiens (EAW58624); horse, E. caballus (XP_003364007); pig, S. scrofa (ACF17563); sheep, O. aries (AAA31507); cattle, B. taurus (XP_876525); cat, Felis catus(NP_001095910); and bats, P. alecto (ELK15819), Eidolon helvum (AFH73816), M. davidii (ELK26495), M. brandtii (EPQ20230), M. lucifugus (GL429988:1422681:1423811:1), and E. serotinus (KF758764). A triangle (▲) indicates a bat species.