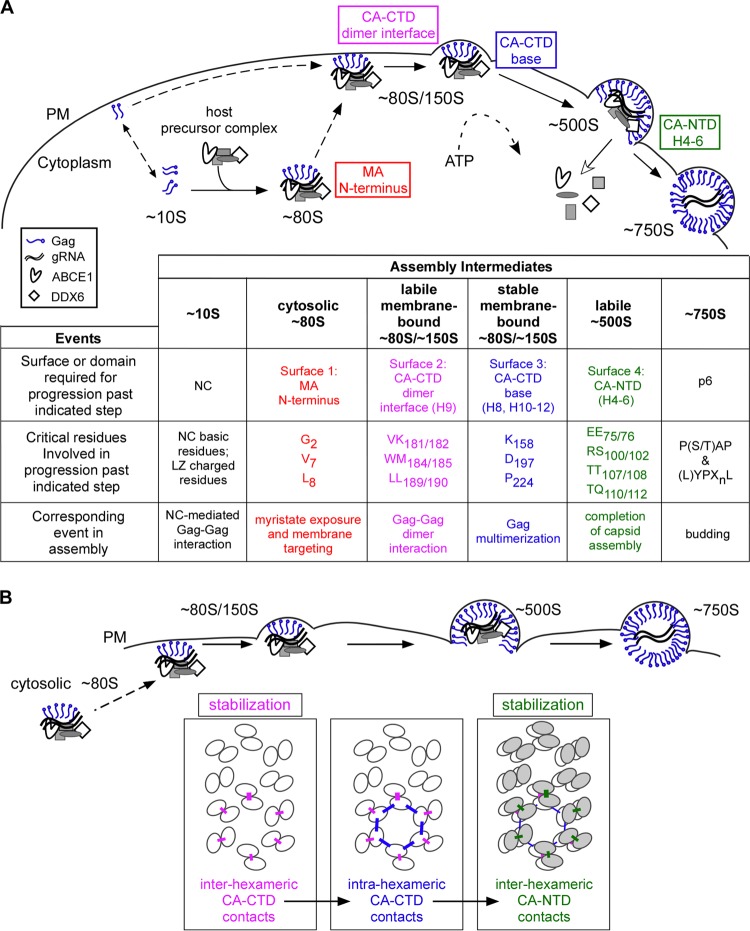
FIG 14.
A temporospatial map of HIV-1 capsid assembly in cells. (A) Temporospatial map of HIV-1 assembly highlighting when and where each critical surface of Gag plays a role in the pathway. Assembly begins when newly synthesized Gag first forms the ∼10S assembly intermediate. Progression past the ∼10S intermediate requires Gag oligomerization mediated by either NC or a leucine zipper (LZ) (42). Formation of the cytosolic ∼80S assembly intermediate results when oligomerized ∼10S Gag co-opts a host precursor complex containing the cellular enzymes ABCE1 and DDX6 (43). The ∼80S intermediate targets to the membrane, where it undergoes continued multimerization to form the ∼150S and ∼500S intermediates. ABCE1 and DDX6 dissociate from the immature capsid upon completion of assembly (40, 43, 46), and release of the budding immature capsid requires residues that interact with cellular factors involved in budding, as shown by others (reviewed in reference 3). The chart shows domains/surfaces and critical residues required for progression past each step in the assembly pathway. (B) A model for when three distinct CA-CA interfaces (identified in the high-resolution structure of a completed immature capsid [29]) are formed during assembly. Ovals represent the individual CA subdomains that form the hexameric lattices in the assembling, immature capsid, in which CA-CTD subunits (white ovals) form the lower hexameric lattice and CA-NTD subunits (gray ovals) form the upper hexameric lattice. The three distinct inter- and intrahexameric interfaces in these lattices are shown as colored lines. These three interfaces involve residues that are identical or adjacent to residues analyzed here on the three CA surfaces and are colored accordingly. In this model, the interhexameric CA-CTD contacts (pink), mediated by residues on the CA-CTD dimer interface, are formed upon or just after membrane targeting of the ∼80S intermediate. The intrahexameric CA-CTD contacts (blue), mediated by residues within the CA-CTD base, form at the membrane and are required for multimerization of assembling Gag. The interhexameric CA-NTD contacts (green), mediated by residues within the CA-NTD H4-6 surface, form late during assembly, just prior to completion of the immature capsid. The two interhexameric CA-CA interfaces promote stability of the assembling capsid at two distinct steps in the assembly pathway.