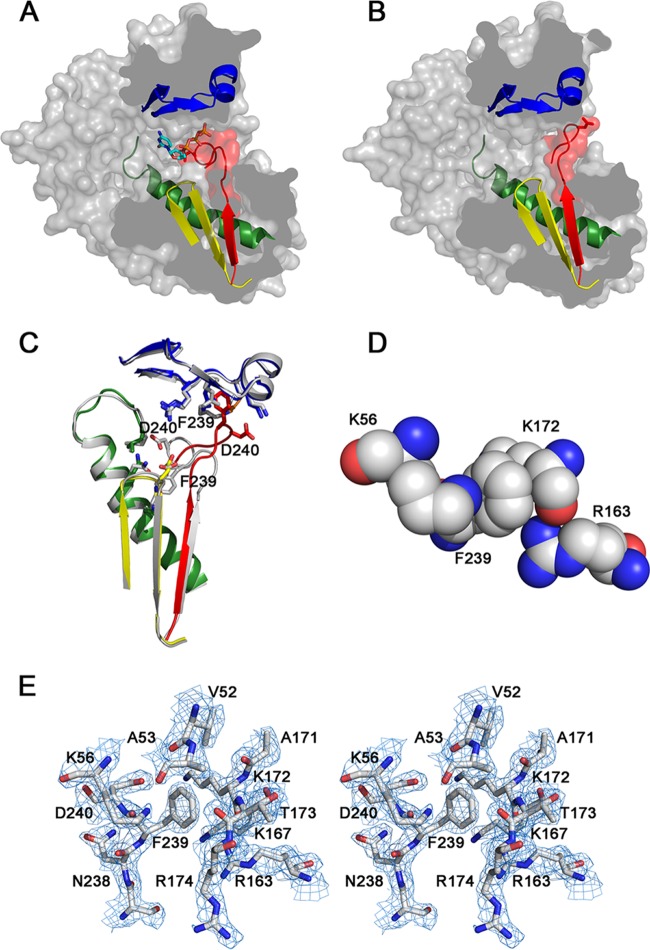
FIG 4.
Structural details around the altered conformation of motif A. (A and B) Side views of the RdRp surface representation from C2 (A) and I4122 (B). The surface has been trimmed to expose the three channels through which the different substrates and products of the polymerization reaction enter or leave the active site. The structural elements that support motifs A, B, and C are also shown as ribbons (the colors are the same as those described in the legend to Fig. 2). (C) Structural superimpositions of the C2 (gray) and I4122 structures showing the organization of motifs A, B, C, and F. The amino acids involved in intramolecular contacts stabilizing the two different conformations are shown as sticks. Residues Phe339 and Asp240, showing the largest displacements, are explicitly labeled. (D) Detail of the binding interactions of residue F239. The aromatic ring of Phe239 forms a cation-π interaction with the ε-amino group of the Lys56 side chain and establishes additional interactions with residues Lys172 and Arg163 from motif F. (E) Stereo view of the electron density map around residue Phe239 of motif A. Stereoview of a weighted 2Fo-Fc Fourier map, contoured at 1.5 σ, with the model placed inside (balls and sticks are colored in atom type code).