FIG 9.
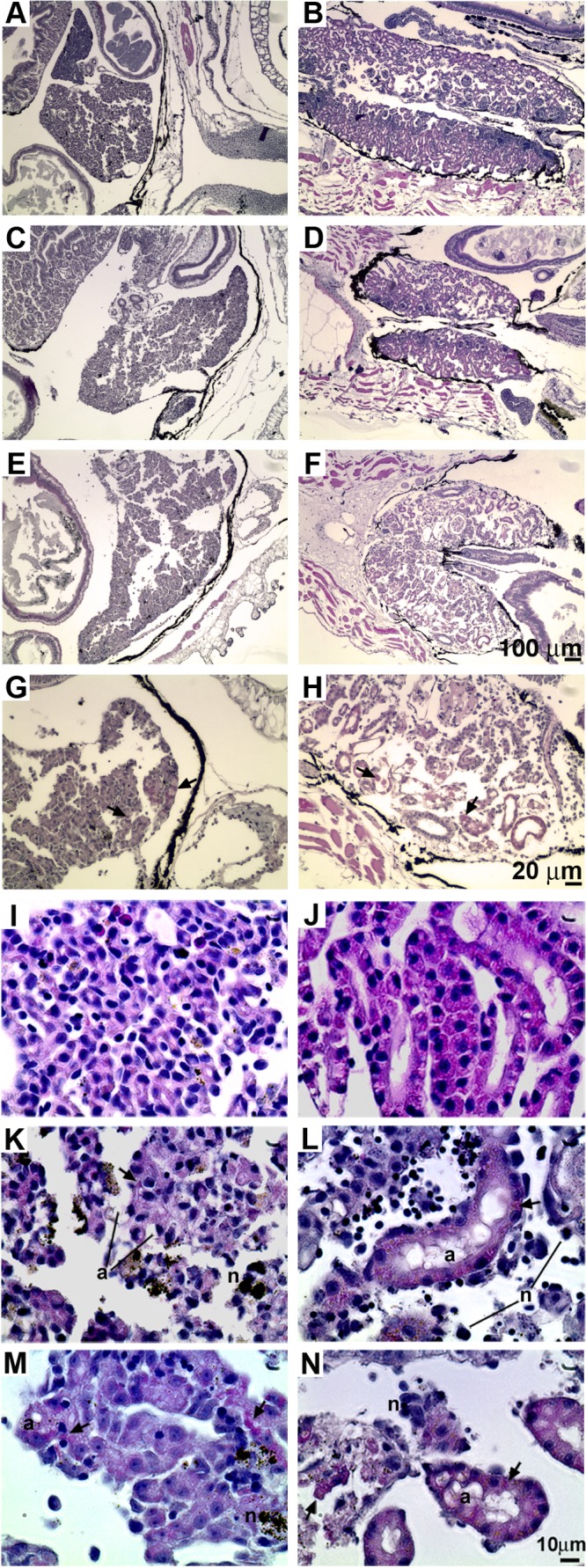
Pretreatment of tadpoles with rXlIFN does not prevent FV3 infection-induced liver and kidney damage. Tadpoles were preinjected with 500 ng of total rXlIFN or an equal volume of the vector control and 8 h later were infected with FV3 or mock infected by APBS injection. Animals were reared until they displayed characteristic signs of terminal infection, sacrificed, and prepared for histology analysis. The cellular compositions were as follows: vector, APBS, liver (A); vector, APBS, kidney (B); rXlIFN, FV3, liver (C); rXlIFN, FV3, kidney (D); vector, FV3, liver (E); vector, FV3, kidney (F); higher magnification, vector, FV3, liver (G); and higher magnification, vector, FV3, kidney (H). Arrows, intracytoplasmic inclusions characteristic of ranavirus-induced pathology. (I to N) Pretreatment of tadpoles with rXlIFN does not prevent FV3 infection-induced cellular damage, necrosis, and apoptosis. Tadpoles were preinjected with rXlIFN (500 ng) or the vector control 8 h before infection with FV3. Animals were reared until they displayed characteristic signs of terminal infection, sacrificed, and prepared for histology analysis. The cellular compositions were as follows: vector, APBS, liver (I); vector, APBS, kidney (J); rXlIFN, FV3, liver (K); rXlIFN, FV3, kidney (L); vector, FV3, liver (M); and vector, FV3, kidney (N). Arrows, FV3-induced intracytoplasmic inclusions; n, necrotic cells; a, apoptotic cells. Bars, 100 μm (A to F), 20 μm (G, H), and 10 μm (I to N).
