FIG 1.
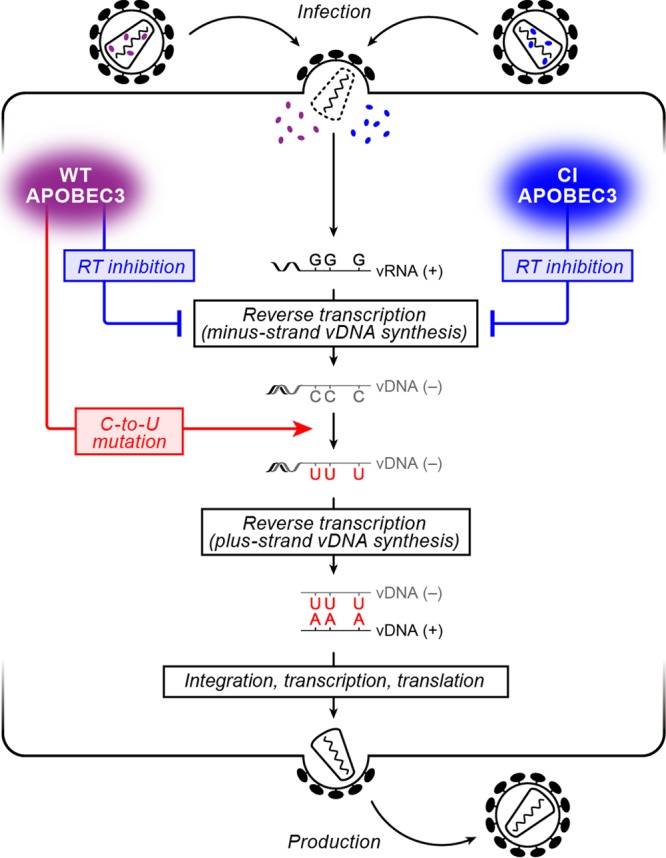
Schematic diagram of the HIV-1 life cycle and the antiviral effect of APOBEC3 proteins. (Left) Incoming WT APOBEC3 proteins (purple) cause (i) the inhibition of the viral RT process independent of their deaminase activity (blue arrow) and (ii) deaminase activity-dependent C-to-U mutations in minus-strand viral DNA (vDNA) resulting in G-to-A mutations in plus-strand vDNA (red arrow), both of which lead to the abrogation of viral replication; (Right) on the other hand, incoming CI APOBEC3 proteins (blue) cause only the inhibition of the viral RT process independent of their deaminase activity (blue arrow).
