FIG 6.
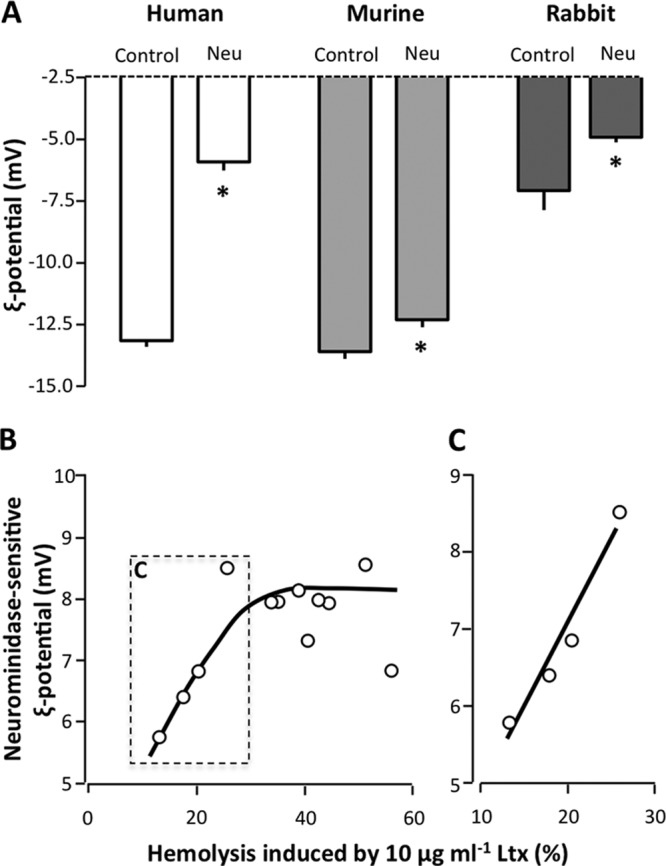
Effect of neuraminidase on the ζ potentials of human, murine, and rabbit erythrocytes. (A) Neuraminidase treatment of human, murine, and rabbit erythrocytes decreases the ζ potential. The erythrocytes were preincubated with or without (control) neuraminidase (60 mU ml−1) for 60 min at 37°C with shaking (250 rpm). (B) Association between the degree of LtxA-induced hemolysis (sensitivity to LtxA) and neuraminidase-sensitive ζ potentials (negative charge induced by sialic acid). In individuals where 10 μg ml−1 LtxA causes only ∼10 to 30% hemolysis, there is a proportional association between the degree of hemolysis and the neuraminidase-sensitive ζ potentials. (C) The initial values fitted to the line y = 0.217x − 12.8 (r = 0.96, P = 0.02). The ζ potential measurements were conducted at 25°C. *, statistical difference from the control (P < 0.05).
