FIG 3.
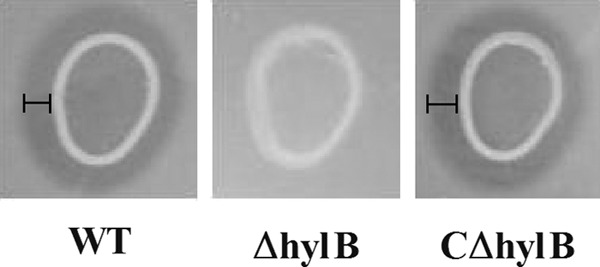
Variation in the ability of the wild-type (WT), hylB mutant (ΔhylB), and complemented (CΔhylB) strains of S. agalactiae to degrade hyaluronic acid. Degradation of the hyaluronic acid was detected as a clear zone (labeled areas) resulting from acetic acid precipitation of a complex of albumin and nondegraded hyaluronic acid. Assays were conducted at least twice.
