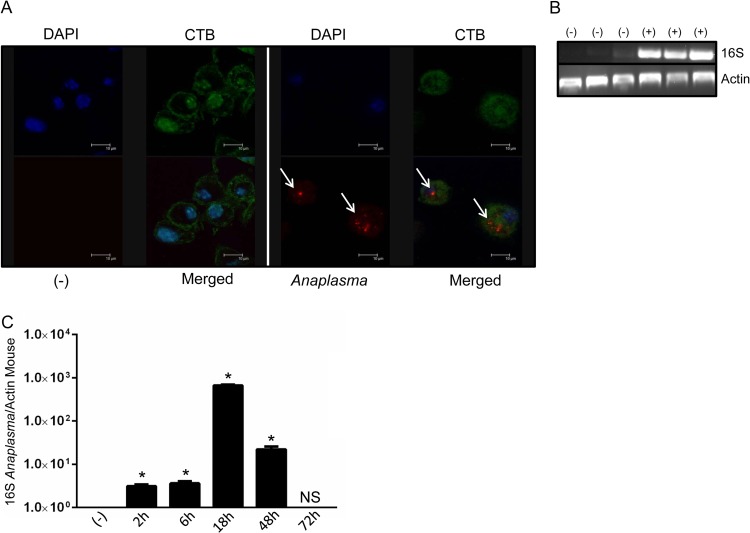
FIG 1.
A. phagocytophilum survives transiently inside macrophages. (A) BMDMs (1 × 106) from C57BL/6 mice were stimulated for 24 h with the wild-type A. phagocytophilum strain HZ (MOI = 50) and stained with cholera toxin subunit B (CTB; green), DAPI (blue), and an antibody against A. phagocytophilum (red; white arrows). (B) BMDMs (1 × 106) from C57BL/6 mice were stimulated for 24 h with the wild-type A. phagocytophilum strain HZ (MOI = 30). Ninety minutes after infection, gentamicin (50 μg/ml) was added to the medium to eliminate extracellular bacteria. Cells were washed extensively with PBS, and the A. phagocytophilum load was measured by PCR, as judged by the 16S rRNA gene. Three representative samples of infected (+) and noninfected (−) cells are shown. (C) Time course series showing A. phagocytophilum loads in macrophages (MOI = 30) after gentamicin protection assays, as judged by the 16S rRNA/mouse actin ratio from quantitative RT-PCR. One-way ANOVA with the Tukey test was used to compare noninfected and infected cells. *, P < 0.05; NS, not significant; (−), nonstimulated cells.