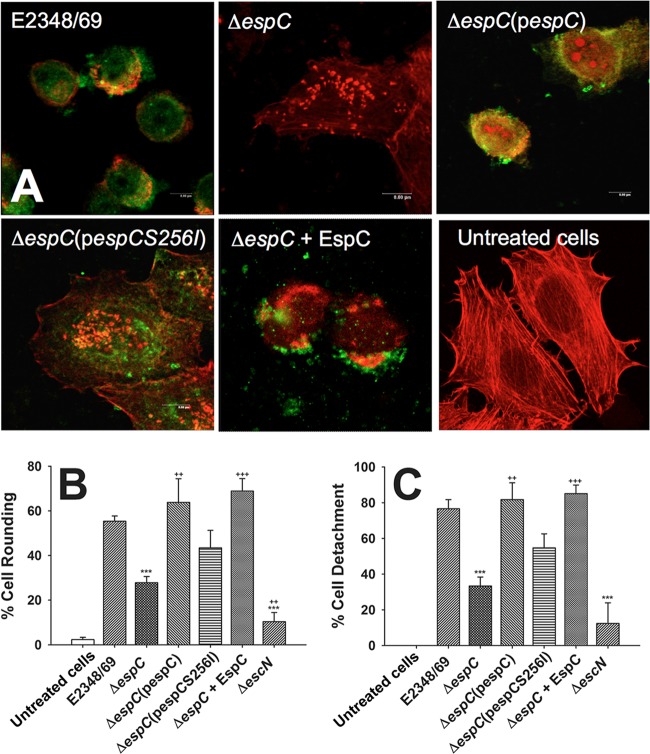
FIG 1.
EspC is required to cause the cytotoxic effect caused by EPEC. (A) HEp-2 cells were infected by either EPEC (strain E2348/69), EPEC ΔespC (mutant ΔespC), EPEC ΔespC(pespC) [complemented ΔespC(pespC) strain], EPEC ΔespC(pespCS256I) [complemented strain with espC gene mutated in the serine protease motif ΔespC(pespCS256I)], or EPEC ΔespC supplemented with purified EspC (ΔespC + EspC strain) for 3 h at an MOI of 10. Infected cells were fixed and permeabilized. Cells were immunostained with anti-EspC antibody, followed by a secondary antibody conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate, and the actin cytoskeleton was detected with rhodamine-phalloidin. Untreated cells were used as negative controls. Slides were observed by confocal microscopy, and in the case of cells treated with EPEC ΔespC(pespCS256I) only a middle optical section is shown to demonstrate that EspCS256I is internalized as the native protein. (B and C) Quantification of cell rounding and cell detachment. After cell treatments as described in panel A, the numbers of rounded cells and detached cells were quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Results are means plus standard deviations of three independent experiments. A P value of <0.005 was considered significant. ***, P < 0.001 (E2348/69 versus ΔespC or ΔescN strain); +++, P < 0.001 (ΔespC strain versus ΔespC + EspC strain); ++, P < 0.005 [ΔespC strain versus ΔespC(pespC) or ΔescN strain].