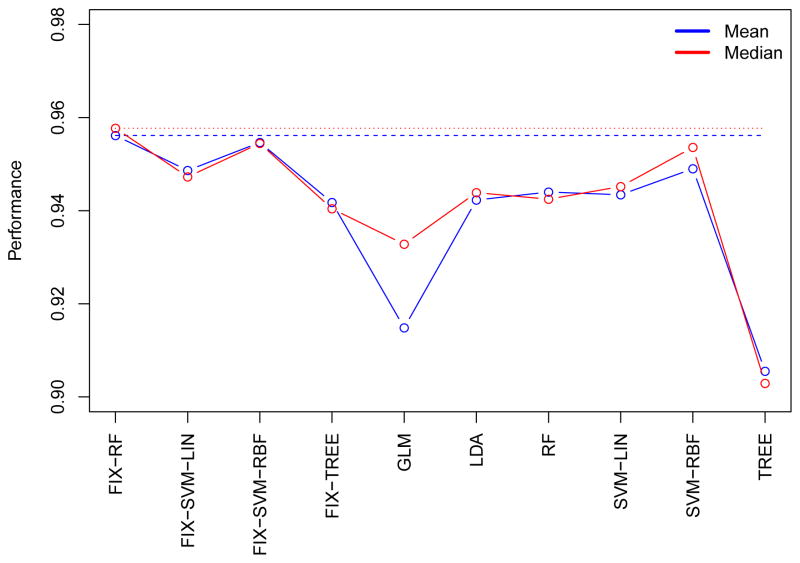
Figure 9.
FIX-RF and FIX-SVM-RBF outperform the commonly-used classifiers on a broad set of rFMRI datasets that cover a board range of data-acquisition/-quality scenarios, common in rFMRI. In the figure, classifiers are shown on the x-axis, and the y-axis shows the average accuracy across all datasets. For each dataset, accuracy is defined as the average of subject-wise (TPR+TNR)/2 (see Section 2.5), where TPR and TNR denote the true positive and true negative rates, respectively. The thick blue and red lines show the mean and median of accuracy across datasets, respectively, and dashed blue and red lines shows the best classifier’s (i.e., FIX-RF) performance in terms of its mean and median, respectively. Thus, on average, FIX is expected to outperform other classifiers, and the best simple classifier next to FIX is SVM-RBF.