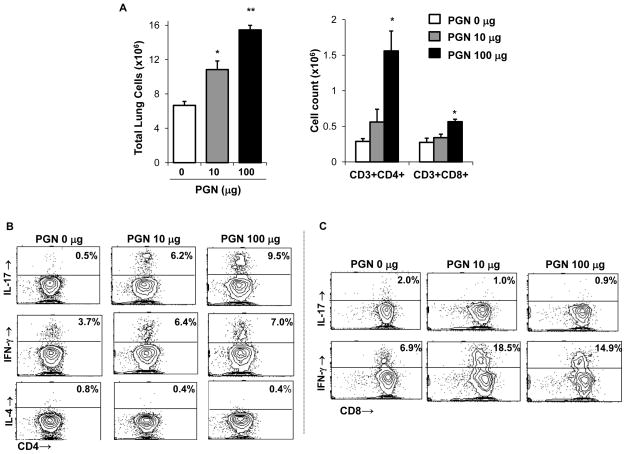
Figure 4. Repetitive intranasal challenge with peptidoglycan (PGN) induces a Th1/Th17-polarized lung cell phenotype.
C57BL/6 mice were repetitively exposed to PGN (10 and 100 μg) or saline for 3 wk, whereupon lung-associated cells were stained for CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+ and T cells and analyzed by FACS. A, Results represent mean ± SEM (N=6 mice/group) of total lung cells, CD3+/CD4+ and CD3+/CD8+ T cells (percentage of cell type x total lung cell count). Statistical difference as compared to saline control (PGN 0 μg) is denoted by asterisk (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). CD4+ and CD8+ T cells pooled from 3 animals and isolated by FACS were immediately stimulated ex vivo with PMA + ionomycin for 4 h, and stained for IL-17, IFN-γ, and IL-4 to demonstrate cytokine profiles. A representative contour plot depicting cytokine staining of isolated CD4+ T cells (B) and CD8+ T cells (C) of one of three independent experiments is shown.