Figure 9.
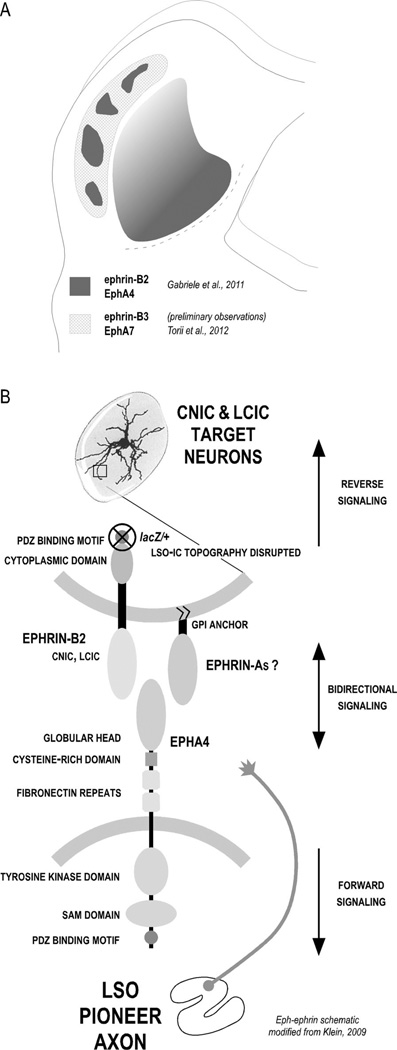
Summary of known Eph-ephrin IC expression and potential signaling model for LSO-IC projections. A: Schematic of Eph-ephrin protein expression in neonatal mouse leading up to the onset of hearing. EphA4 and ephrin-B2 are coexpressed in LCIC modules and graded across the CNIC. Additional experiments are ongoing to determine whether their LCIC modular expression is superimposed or complementary. In contrast, preliminary observations suggest that ephrin-B3 is absent in the CNIC and most concentrated in nonmodular LCIC zones, similar to what has been reported for EphA7 (Torii et al., 2012). Though not noted here, expression of each of these proteins is significantly downregulated as experience ensues (see Miko et al., 2007; Gabriele et al., 2011). B: Potential Eph-ephrin interactions in ordering developing LSO axons with target IC neurons. EphA4-expressing LSO axons likely encounter target IC neurons that express ephrin-B2 (CNIC and LCIC). Our ephrin-B2lacZ/+ mutant is capable of forward signaling (into the Eph-expressing axons; bottom) yet, because of a truncated cytoplasmic domain, is incapable of reverse signaling (into the ephrin-expressing target IC cell; top). Topographic mapping is disrupted in these mutants, but layered and modular IC pattern formation remains unaffected.