Figure 4.
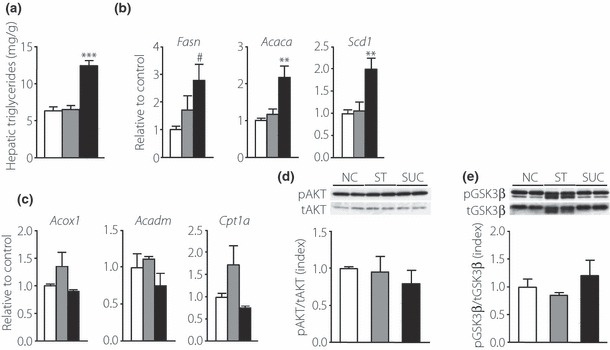
Effects of carbohydrates on hepatic lipid metabolism. (a) Hepatic triglyceride content in the livers of mice fed a normal chow diet (NC; white bars, n = 6), a high‐starch diet (ST; gray bars, n = 8) or a high‐sucrose diet (SUC; black bars, n = 9). (b) Messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression of the lipogenic enzymes fatty acid synthase (Fasn), acetyl‐CoA carboxylase α (Acaca) and stearoyl‐CoA desaturase 1 (Scd1) and (c) the lipolytic enzymes acyl‐CoA oxidase (Acox1), medium‐chain acyl‐CoA dehydrogenase (Acadm), and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α (Cpt1a) in the livers of mice fed a NC (white bars, n = 6), a ST (gray bars, n = 7–8) or a SUC (black bars, n = 5–7). The abundance of mRNA relative to 36B4 mRNA was determined using real‐time polymerase chain reaction, and is expressed as a fold increase relative to the control. (d, e) Insulin‐induced phosphorylation of AKT and glycogen synthase kinase‐3β (GSK‐3β) in the liver. Mice were injected intravenously with insulin. Liver was extracted 3 min after the injection, and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (d) Representative immunoblots and quantification of the phosphorylation of AKT by insulin. AKT phosphorylation is expressed as the ratio of phospho‐AKT (pAKT) relative to the total amount of AKT. (e) Representative immunoblots and quantification of the phosphorylation of GSK‐3β by insulin. GSK‐3β phosphorylation is expressed as the ratio of phospho‐GSK‐3β (pGSK‐3β) relative to the total amount of GSK‐3β. White, gray and black bars indicate data from mice fed a NC (n = 3), a ST (n = 3) or a SUC (n = 3), respectively. Values are mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared with the NC‐ and ST‐fed mice. #P < 0.05 compared with the NC‐fed mice. tAKT, total AKT; tGSK‐3β, total GSK‐3β.
