Figure 1.
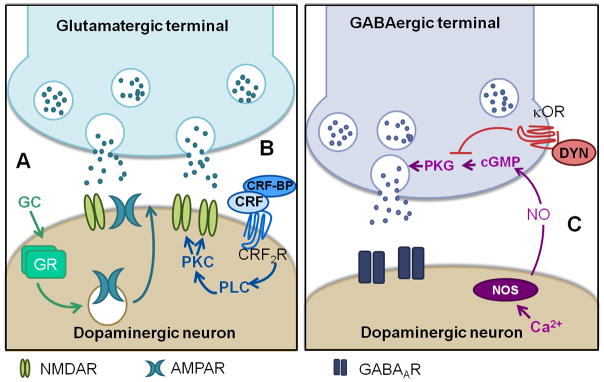
Modulation of VTA synaptic plasticity by stress systems. A) At excitatory synapses, stress-induced activation of glucocorticoid receptors leads to an increase in the AMPA and NMDA ratio. B) CRF potentiates NMDA currents through activation of CRF2 receptors and downstream activation of PLC and PKC. C) Inhibitory synapses are potentiated via the retrograde messenger nitric oxide and activation of cGMP signaling. This plasticity is blocked by stress through activation of kappa opioid receptors. From (Saal et al., 2003; Ungless et al., 2003; Nugent et al., 2007; Daftary et al., 2009; Nugent et al., 2009; Niehaus et al., 2010; Graziane et al., 2013)
GC: glucocorticoid, GR: glucocorticoid receptor, CRF: corticotrophin releasing factor, CRF-BP: CRF-binding protein, CRF2R: CRF receptor type 2, PLC: phospholipase C, PKC: protein kinase C,NOS: nitric oxide synathase, NO: nitric oxide, cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate, κOR: kappa opioid receptor, dyn: dynorphin, PKG: protein kinase G
