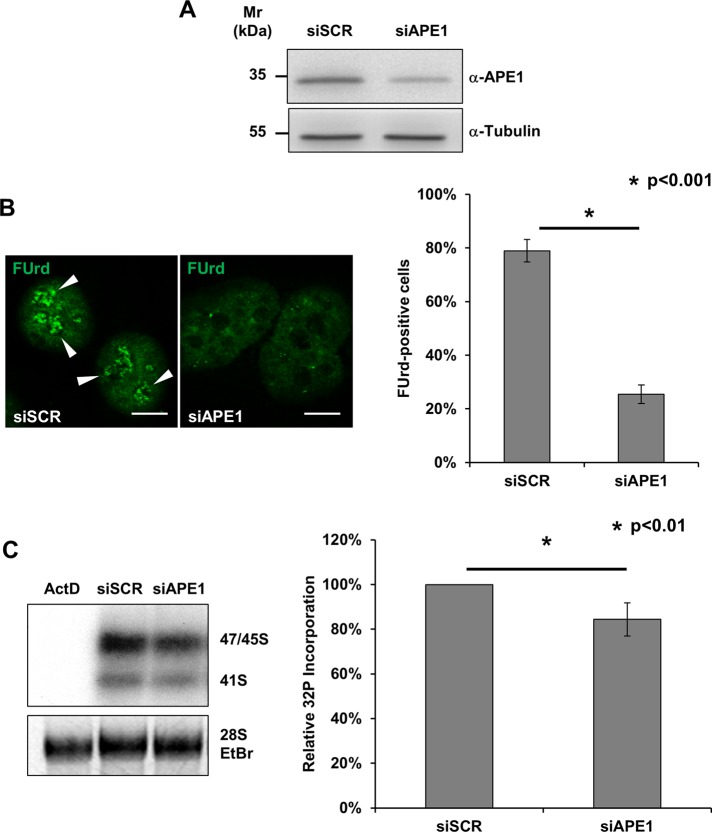
FIGURE 8:
Depletion of APE1 leads to nucleolar impairment. (A) Representative Western blot analysis on HeLa cells treated with either a scrambled siRNA (siScr) or an APE1-targeting siRNA (siAPE1) shows the efficiency of APE1 knockdown. Tubulin was used as loading control. (B) FUrd labeling of siScr- and siAPE1-treated HeLa cells. Left, representative immunofluorescence showing the preferential accumulation of FUrd within transcriptionally active nucleoli only in APE1-proficient cells (white arrowheads). Bars, 8 μm. Right, histogram reporting the average FUrd nucleolar incorporation efficiency in siScr and siAPE1 cells. Values reported express the average amount of FUrd-positive cells ± SD from at least three independent experiments. (C) [32P]phosphate metabolic labeling of nascent rRNA transcripts in HeLa cells treated with siScr, siAPE1, or actinomycin D (as positive control) reveals the nucleolar impairment in APE1-depleted cells. Cells were transfected with siRNAs and 48 h later pulsed for 1 h with [32P]orthophosphate as described in Materials and Methods. Left panel, total RNA was extracted and the amount of labeled rRNA precursors was measured through autoradiography. Ethidium bromide staining was used as loading control. Right, histogram reporting the average [32P]phosphate incorporation into the 47S precursor in siScr and siAPE1 cells. Values reported express the mean incorporation ± SD from at least three independent experiments. siScr was used as reference sample.