FIGURE 1:
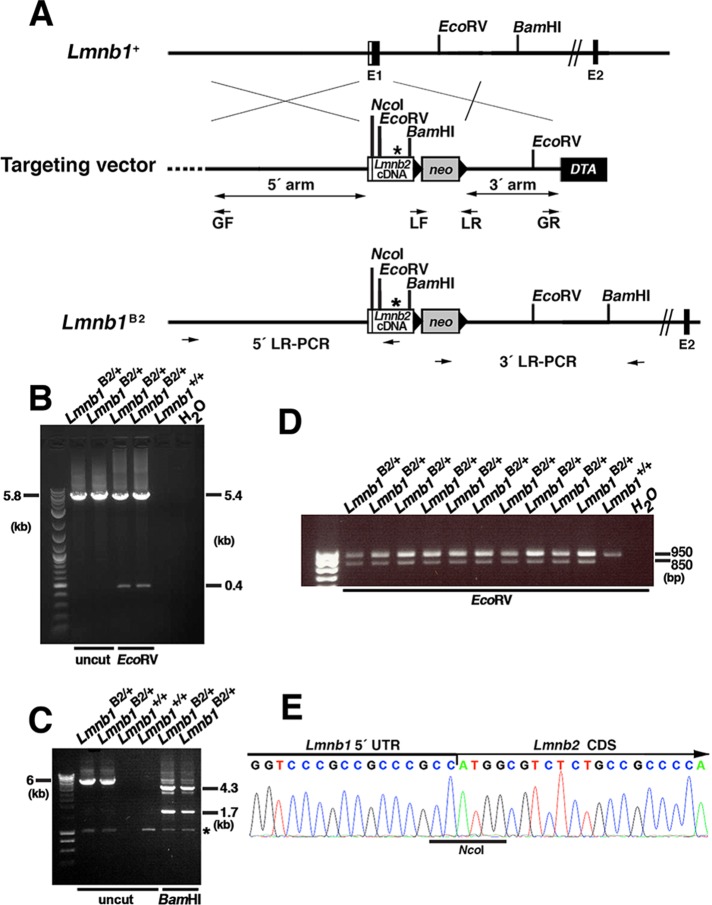
Generation of the Lmnb1B2 allele, which yields lamin B2 from the Lmnb1 locus. (A) Map of the Lmnb1 locus and the targeting vector, which was designed to introduce a Lmnb2 cDNA into the translational start site in exon 1 of Lmnb1 (at an NcoI site). The Lmnb2 cDNA was modified to introduce a new EcoRV site and remove an existing SacI site (depicted by an asterisk), making it possible to distinguish Lmnb1B2 transcripts from those of the endogenous Lmnb2 locus. Exons are depicted as black boxes (E1 and E2); the noncoding region of exon 1 is in white. Black arrowheads indicate the loxP sites. The neo cassette is shown as a gray box; a diphtheria toxin (DTA) counterselection cassette is shown as a black box. The primers used for recombineering (GF, GR, LF, and LR) are indicated. The primers used for 5′ long-range PCR (5′ LR-PCR) and 3′ long-range PCR (3′ LR-PCR) are indicated by arrows. (B) Screening of ES cell clones by 5′ long-range PCR. A 5.8-kb fragment was amplified from the Lmnb1B2 allele; the identity of the fragment was confirmed by EcoRV digestion (yielding 5.4-and 0.4-kb fragments). (C) Screening of ES cell clones by 3′ long-range PCR. A 6-kb DNA fragment was amplified from the Lmnb1B2 allele; the identity of the fragment was confirmed with BamHI digestion (yielding 4.3- and 1.7-kb fragments). A nonspecific band is indicated by an asterisk. (D) EcoRV digestion of a 950–base pair Lmnb2 RT-PCR fragment (amplicon from exons 1–7 of Lmnb2) from Lmnb1B2/+ and Lmnb1+/+ ES cells. Lmnb2 RT-PCR DNA fragments from the Lmnb1B2 allele (but not from the endogenous Lmnb2 allele) were cleaved by EcoRV (yielding an 850–base pair fragment). (E) DNA sequencing chromatogram of an RT-PCR fragment from the Lmnb1B2 allele showing the junction between the Lmnb1 5′ UTR and Lmnb2 coding DNA sequences (CDS).