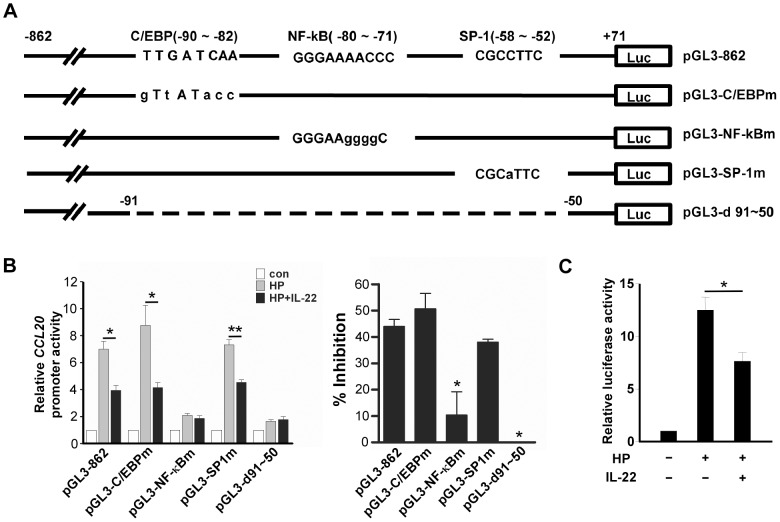
Figure 5. The NF-κB binding site in the CCL20 promoter is critical for the IL-22-attentuated CCL20 expression.
A, Schematic representation of mutated or deleted CCL20 reporter constructs. Nucleotide substitutions are indicated in lower case and the deleted region is indicated as dash line. B, Inhibitory effects of IL-22 on CCL20 promoter activities. Left panel, AGS cells were co-transfected with the indicated CCL20 promoter constructs and pRL-TK Renilla luciferase plasmid. At 48 h after transfection, cells were infected with H. pylori in the presence or absence of IL-22 and the relative luciferase activity was measured. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *, p<0.05, **, p<0.005 for H. pylori + IL-22 versus H. pylori only. Right panel, the inhibitory efficiency (% inhibition) were calculated as described in Fig. 4B. *, p<0.05 versus pGL3-862, pGL3/EBPm or pGL3-SPm. C, Inhibitory effects of IL-22 on a promoter containing NF-κB binding sites. AGS cells were co-transfected with pGL4.32 NF-κB luciferase reporter and pRL-TK Renilla luciferase plasmid. At 48 h after transfection, cells were infected with H. pylori in the presence or absence of IL-22 and the relative luciferase activity was measured. Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *, p<0.05 for H. pylori + IL-22 verses H. pylori only.