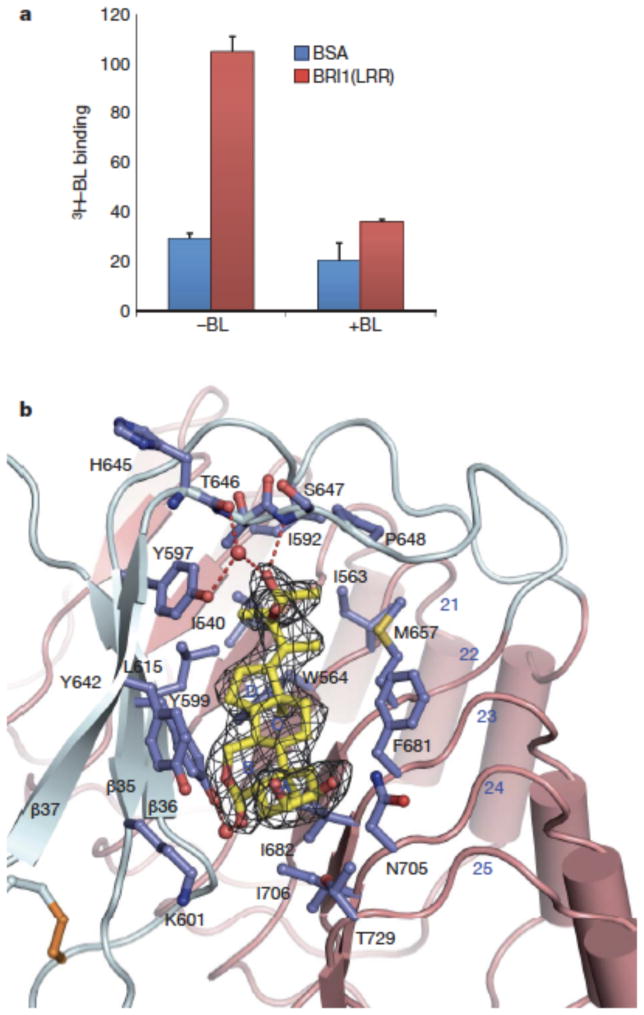
Fig. 3. BL binds a hydrophobic groove between the ID and the inner surface of LRRs.
a. [3H]-BL binding activity of BRI1-LRR. About 1 mg ml−1 BRI1-LRR-His (red bar) or BSA as control (blue bar) was incubated with 20 nM [3H]-BL in the absence (−BL) or presence (+BL) of 20 μM unlabelled BL. BRI1-bound [3H]-BL was recovered using nickel beads and quantified by scintillation counting. Data represent the average of triplicate assays and error bars are standard deviations.
b. Detailed interactions between BL and BRI1-LRR. Shown in mesh is omit electron density (2.5 δ) around BL. The ID and LRRs are colored in slate and salmon, respectively. The side chains from both the ID and LRRs are shown in slate. Red spheres represent oxygen atoms of water molecules. The three β–strands from the ID are labeled.