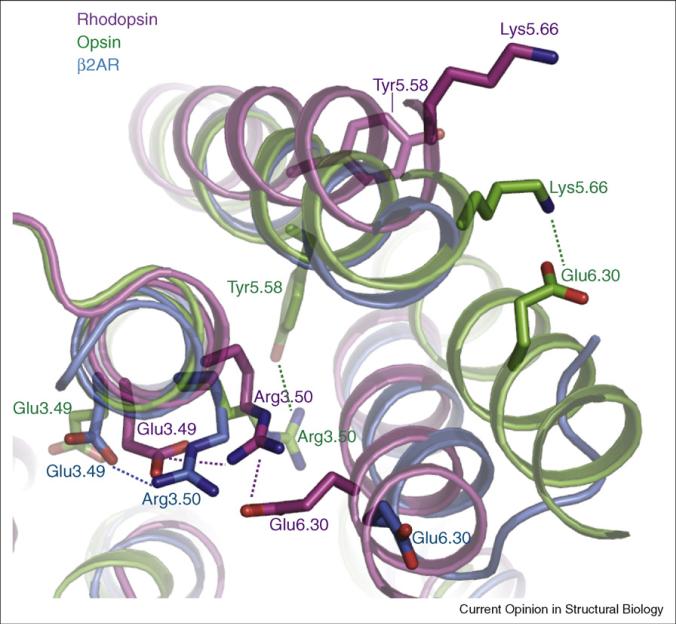
Figure 1.
An overlay of dark rhodopsin (purple; PDB 1gzm), low pH opsin (green; PDB 3cap), and carazolol-bound β2AR–T4L (blue; PDB 2rh1) in the vicinity of the ionic lock. In dark rhodopsin, Arg1353.50 in the conserved D/ERY sequence near the cytoplasmic end of TM3 forms a salt bridge with Glu2476.30 at the cytoplasmic end of TM6. Arg3.50 is further stabilized by a salt bridge to the preceding conserved acid at position 3.49 in both rhodopsin and β2AR. In opsin, Arg1353.50 interacts with Tyr2235.58 in TM5, and Glu2476.30 forms a salt bridge with Lys2315.66. The homologous ionic lock residues Arg1313.50 and Glu2686.30 from the β2AR are also shown. The amino acids are numbered using the Ballesteros–Weinstein system. Within each helix is a single most conserved residue among the class A GPCRs. This residue is designated x.50, where x is the number of the transmembrane helix. All other residues on that helix are numbered relative to this conserved position.