Figure 12.
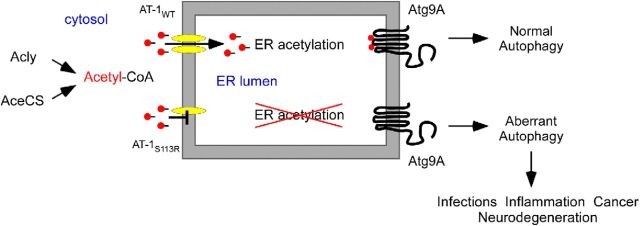
Schematic interpretation of our results. WT AT-1 (AT-1WT) is a homodimer in the ER membrane, where it ensures constant influx of acetyl-CoA into the lumen of the organelle. SPG-associated AT-1 (AT-1S113R) is unable to form homodimers and, as a result, is devoid of transport activity. Animals heterozygous for the mutation have reduced influx of acetyl-CoA into the ER lumen, which results in deacetylation (or nonacetylation) of Atg9A and aberrant induction of autophagy. The aberrant levels of autophagy lead to propensity to infections, diffuse inflammation, propensity to cancer, and neurodegeneration of both the PNS and CNS. Animals homozygous for the mutation suffer from early developmental arrest.