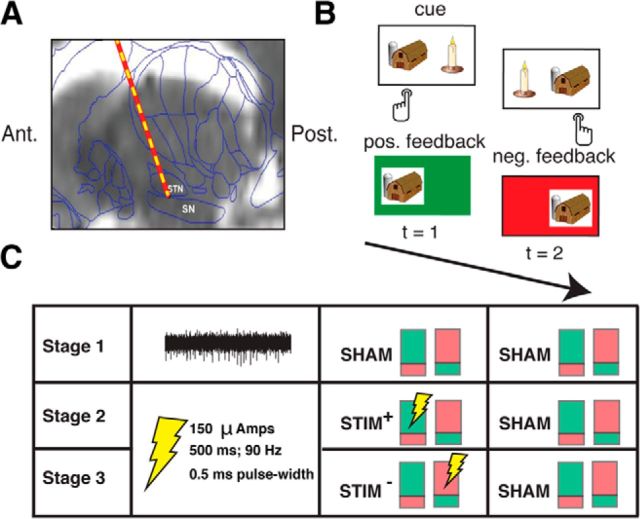
Figure 1.
A, Intraoperative targeting of SN. During DBS surgery, a microelectrode is advanced into the SN to map the ventral border of the STN. An example preoperative MRI scan (sagittal view) overlaid with a standard brain atlas and estimated microelectrode position is shown (Jaggi et al., 2004; Zaghloul et al., 2009). B, Reinforcement learning task. During surgery, 11 subjects performed a two-alternative probability learning task with inconsistent stimulus-response mapping. C, Experimental design. During each stage of the session (50 trials each), subjects sampled reward probabilities of two item pairs that were matched in relative reward rate. Each pair of colored rectangles depicts an item pair (the green and red shading within each rectangle indicates the probability of positive and negative feedback associated a particular item in the pair, respectively). During Stage 1, we obtained microelectrode recordings from the SN. An example 500 ms high-pass-filtered (>300 Hz) voltage trace is shown. During Stages 2 and 3, we applied electrical microstimulation through the recording microelectrode as depicted, but no longer obtained recordings (see Materials and Methods).