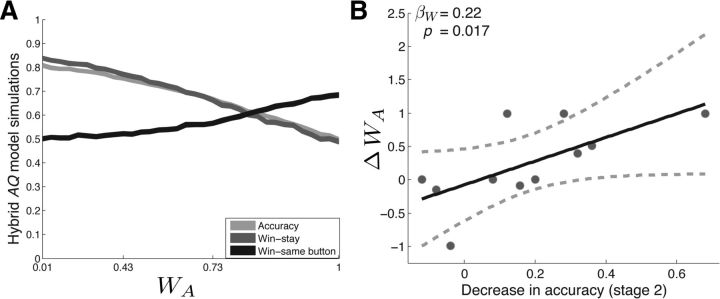
Figure 4.
A, Hybrid AQ learning model. Shown is the simulated behavior of the three-parameter reinforcement learning algorithm (hybrid AQ model) on a two-alternative probability learning task with inconsistent stimulus-response mapping. Accuracy (light gray line), probability of repeating rewarded items (win-stay, dark gray line), and probability of repeating rewarded actions (win-same button, black line) are shown for varying values of the action value weighting parameter (WA). Strengthened action–reward associations were associated with decreases in accuracy and win-stay and increases in win-same button. B, Stimulation-related behavioral changes can be explained by strengthened action–reward associations. We quantitatively fit the hybrid AQ model to subjects' behavior on the STIM+ and SHAM pair during Stage 2. We found that stimulation-related decreases in accuracy showed a significant positive relation with increases in WA, but not α or β. See main text for statistics.