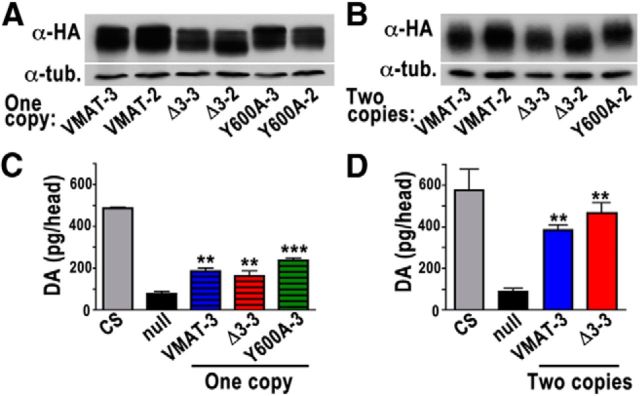
Figure 6.
Protein expression and rescue of amine levels by DVMAT trafficking mutants. A, B, Western blots probed with an antibody to the HA epitope tag in all DVMAT isoforms show DVMAT protein expression in dVMAT P1 null flies expressing one copy (A) or two copies (B) of UAS-DVMAT-wt, UAS-DVMAT-Δ3, or UAS-DVMAT-Y600A transgenes coupled with either one copy (A) or two copies (B) of the da-Gal4 driver, respectively. For UAS-DVMAT-wt, UAS-DVMAT-Δ3, and UAS-DVMAT-Y600A, independent insertions on both the second chromosome (VMAT-2, VMAT-Δ3–2, and VMAT-Y600A-2) and third chromosomes (VMAT-3, VMAT-Δ3–3, and VMAT-Y600A-3) are shown. Tubulin (“tub.”) was used as a loading control (bottom panels). C, D, HPLC with electrochemical detection was used to measure dopamine levels in heads of control CS flies, the dVMATP1 null (null), and dVMATP1 rescued with either one copy (C) or two copies (D) of wt or mutant UAS-DVMAT transgenes on chromosome 3. The dVMATP1 null showed reduced levels of dopamine compared with CS controls. DA levels were partially rescued with one copy of UAS-DVMAT-wt, UAS-DVMAT-Δ3, or UAS-DVMAT-Y600A (all on chromosome 3), and were rescued to near wt levels with two copies of UAS-DVMAT-wt or UAS-DVMAT-Δ3 and two copies of driver (two copies of UAS-DVMAT-Y600A were lethal; mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001, n = 3–5 per genotype. Bonferroni post-test, ***p < 0.001 between null and Y600A in C and **p < 0.01 between null and all other lines in C and D).