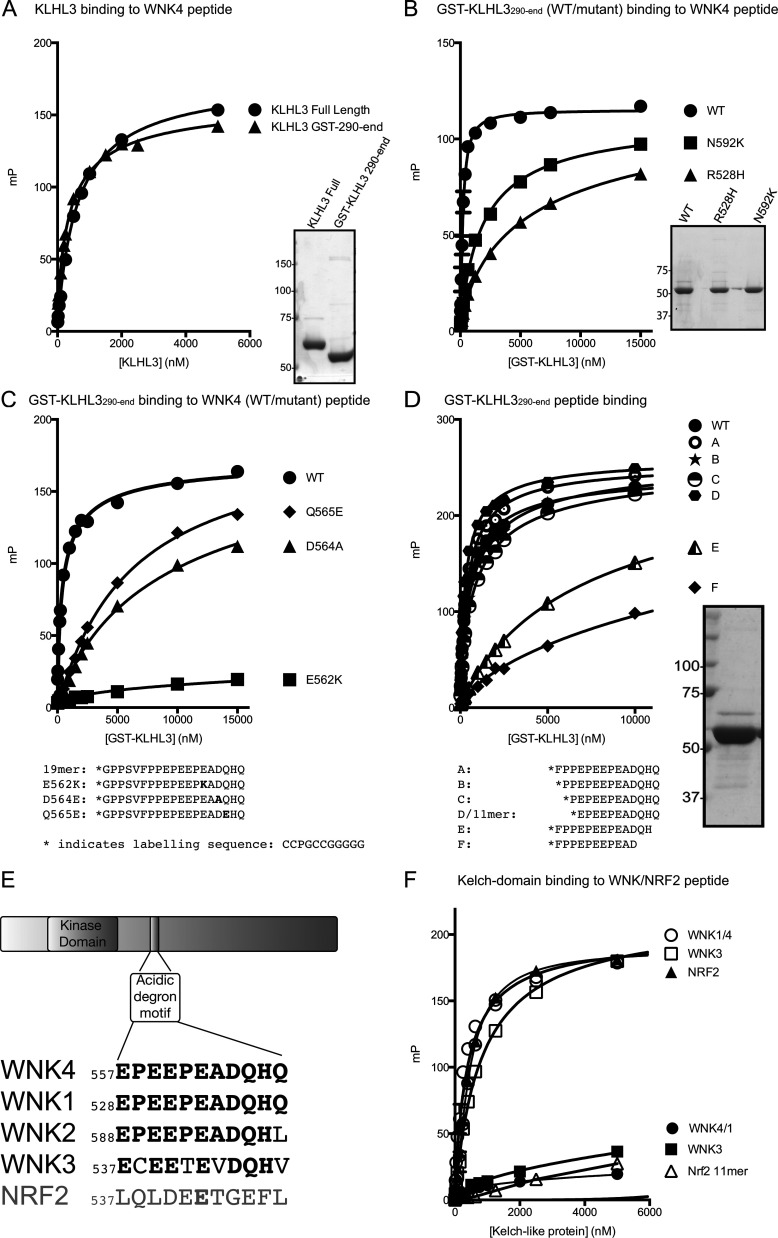
Figure 1. Analysis of KLHL3–WNK interaction by fluorescence polarization.
(A–D and F) Purified KLHL3 was diluted appropriately and mixed at a 1:1 volume ratio with 20 nM Lumino-Green-labelled WNK peptide to the concentration stated in the Figure, with the peptide concentration consistent at 10 nM, and fluorescent polarization measurements were made. Binding curves, assuming one-site-specific binding, were then generated with Prism6 using milli-polarization (mP) units. The determined dissociation constant for each binding experiment is shown in Table 1. The purified KLHL3 proteins used in the binding experiments were analysed on SDS/PAGE and are shown in panels to the right of the binding curve. Molecular masses are indicated on the left of the gels. (A) Comparison of full-length KLHL3 and the isolated Kelch-domain of KLHL3 binding to the 19-residue WNK4 degron peptide (GPPSVFPPEPEEPEADQHQ, residues 549–567). (B) Influence of KLHL3 Gordon's syndrome mutations on WNK4 peptide binding. Purified GST-KLHL3290–587 wild-type, or the point mutants, GST–KLHL3290–587 R528H, GST–KLHL3290–587 N259K, were analysed for their ability to bind the 19-residue WNK4 degron peptide. (C) Effect of WNK4 Gordon's syndrome mutations on KLHL3 binding. Purified GST–KLHL3290–587 wild-type protein was mixed with the 19-residue wild-type (WT) or indicated point mutants (E562K, D564A and Q565E) of the WNK4 degron peptide. The sequences of all peptides used are shown in the bottom panel exclude the N-terminal sequence (CCPGCCGGGG) required for Lumio Green labelling. (D) Impact of shortening the WNK4 peptide on KLHL3 binding. The ability of the indicated WNK4 peptides A–F (the sequences of which are shown below the binding curve) to bind purified GST–KLHL3290–587 protein was evaluated. (E) Location and conservation of degron motif in WNK isoforms. The upper panel displays the domain organisation of WNK isoforms and the location of the degron motif within the C-terminal non-catalytic domain. The lower panel displays an alignment of the degron motif in different WNK isoforms with that of the previously characterized degron motif of the NRF2 transcription factor that interacts with the KEAP1 Kelch-like protein [38]. Identical residues are shaded in black. (F) Evaluation of the ability of WNK1/4, WNK3 and NRF2 degron peptides to interact with GST–KLHL3290–587 (open symbols) and full-length KEAP1 (closed symbols). WT, wild-type.