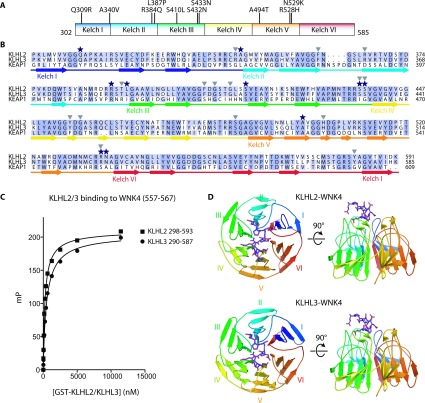
Figure 2. Overview of the KLHL2 and KLHL3 structures and their interaction with the WNK degron motif.
(A) Schematic representation of the Kelch domain (residues 302–585) of KLHL3 with the positions of the dominant Gordon's syndrome-associated mutations illustrated. (B) Sequence alignment of the Kelch domain of KLHL2, KLHL3 and KEAP1, with the secondary structure of KLHL3 indicated. A black star above the amino acid indicates the position of a Gordon's syndrome mutation and a grey triangle indicates key contact residues in the KLHL3–WNK4 structure. (C) Comparison of the binding of the WNK4 degron motif to KLHL2 and KLHL3. Fluorescent polarisation measurements were made as described in Figure 1 and the Materials and methods section. Purified GST–KLHL3290–587 or GST–KLHL2298–593 were mixed with the 11-residue WNK4 (557–567) degron peptide and binding curves were generated. (D) An overview of the KLHL2–WNK4 (top panel) and KLHL3–WNK4 (bottom panel) crystal structures. The Kelch domain is shown in cartoon representation and the WNK4 peptide is shown in purple stick representation.