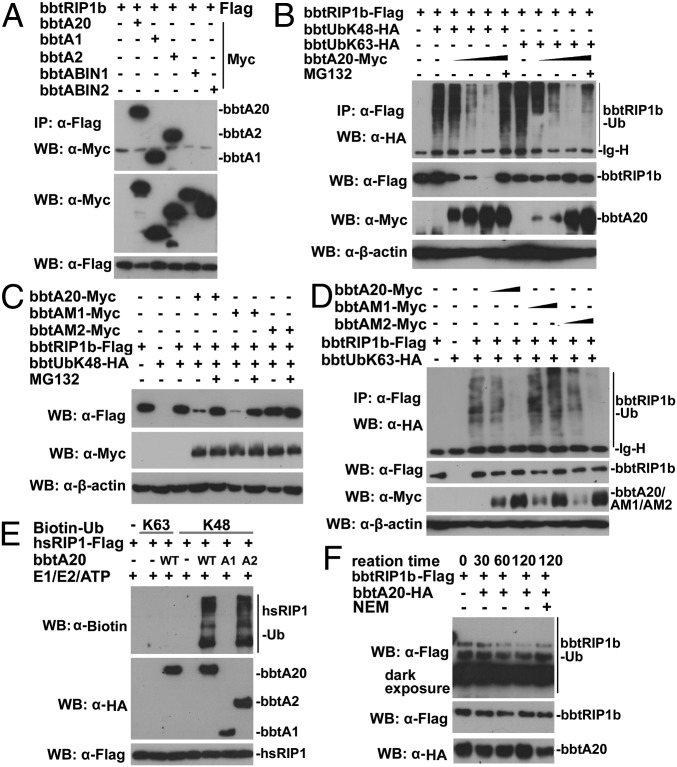
Fig. 5.
BbtA20 is a dual enzyme in removing the K63-linked ubiquitin chains and adding the K48-linked ubiquitination on bbtRIP1b. (A) Co-IP assays assessing the direct interaction between bbtRIP1b and bbtA20 and identifying both OTU and ZnFs of bbtA20 are responsible for the interaction. (B) Cotransfection of bbtA20 promotes bbtRIP1b degradation in HEK 293T cells. Such degradation could be inhibited by addition of MG132. Moreover, cotransfection of bbtA20 removes the K63-linked polyubiquitin chains from bbtRIP1b in a dose-dependent manner. (C) Cotransfection of WT bbtA20 or OTU mutant (bbtAM1), but not ZnF4 mutant (bbtAM2), results in the proteasome-dependent degradation of bbtRIP1b. (D) Cotransfection of WT bbtA20 or bbtAM2, but not bbtAM1, results in a low level of K63-linked ubiquitination, but not degradation, of bbtRIP1b in a dose-dependent manner. (E) In vitro ubiquitination assays showed that both WT bbtA20 and bbtA2 (the ZnFs only) can function as E3 to catalyze the K48-linked ubiquitination of hsRIP1b. (F) In vitro deubiquitination assays indicated that bbtA20 can deubiquitinate the K63-linked ubiquitinated bbtRIP1b. All co-IP experiments were done at least twice.