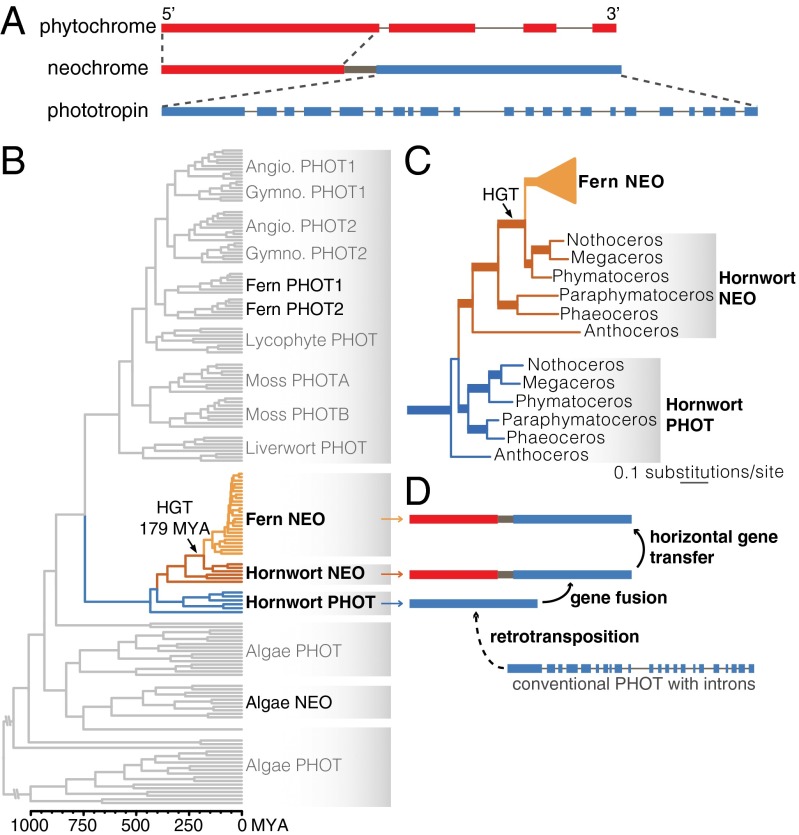
Fig. 1.
The origin of fern neochrome. (A) Neochrome is a chimeric photoreceptor in which the N terminus consists of a phytochrome sensory module fused to an almost complete phototropin sequence at the C terminus. Thick and thin lines represent exons and introns, respectively (length not to scale). (B) Dated phylogeny of phototropin and neochrome, showing neochrome HGT from hornworts to ferns (details are given in SI Appendix, Fig. S5). The blue, brown, and yellow branches represent hornwort phototropin, hornwort neochrome, and fern neochrome, respectively. (C) Portion of the phototropin phylogeny showing relationships of fern neochrome (Fern NEO), hornwort phototropin (Hornwort PHOT), and hornwort neochrome (Hornwort NEO), with highly supported branches thickened (details are shown in SI Appendix, Figs. S1 and S2). (D) A schematic depicting the origin of fern neochrome involving retrotransposition of a phototropin gene (and hence the loss of introns), its fusion with a phytochrome, and HGT from hornworts to ferns.