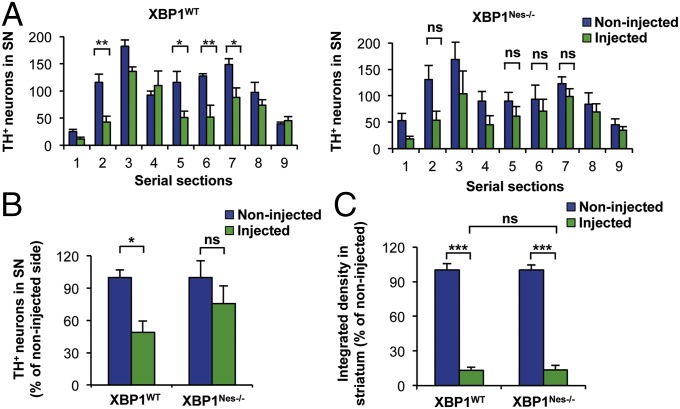
Fig. 1.
Dopaminergic neurons of XBP1-deficient mice are resistant to 6-OHDA–induced neurotoxicity. (A) XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice were injected with 8 μg of 6-OHDA in the right striatum, and after 7 d, dopaminergic neurons (TH+) were quantified by anti-TH immunohistochemistry. Histograms show the number of TH-positive neurons of injected and noninjected sides in 25-μm midbrain serial sections separated by 150 μm and covering the entire SN. The numbers of serial sections indicate the orientation from anterior to posterior (Fig. S1C). (B) Total content of TH-positive somas was quantified in midbrain sections 2, 5, 6, and 7 and presented as a percentage of the noninjected (control) side for the indicated genotypes. (C) 6-OHDA–induced striatal denervation in XBP1WT and XBP1Nes−/− mice. The integrated density of pixel intensity was calculated from images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry covering the entire striatum and is presented as a percentage of the noninjected (control) sides for both genotypes. For all quantifications, data are mean ± SEM (n = 4 per group). Statistical analyses were performed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. ns, not significant.