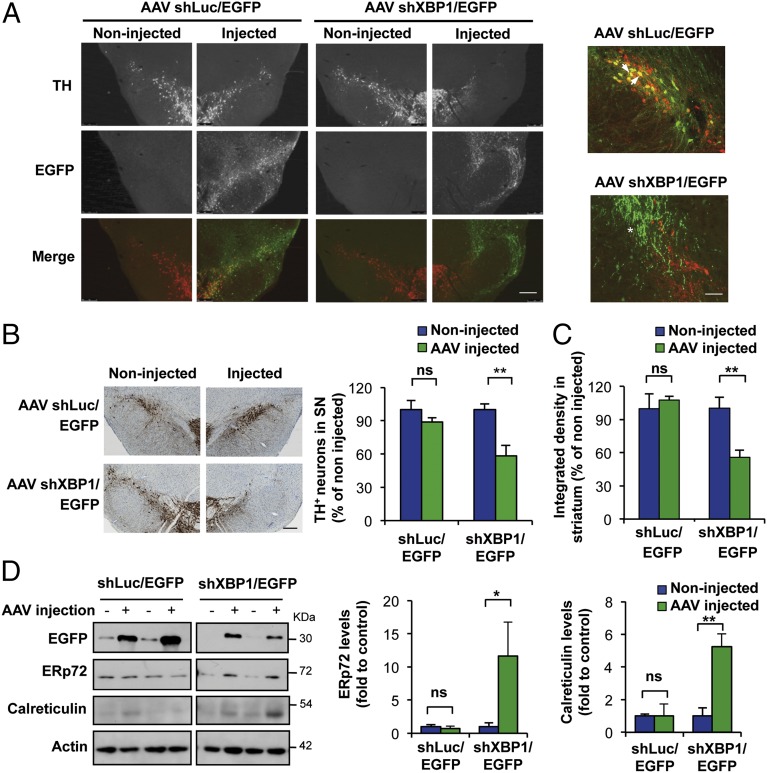
Fig. 3.
XBP1 down-regulation in dopaminergic neurons of adult SNpc induces spontaneous neurodegeneration and chronic ER stress. (A) In WT mice, the SNpc was injected with AAVs carrying a shRNA construct designed against either XBP1 (shXBP1/EGFP) or luciferase (shLuc/EGFP) mRNA by brain stereotaxis. (Left) At 1 mo after the injections, dopaminergic neurons were visualized by TH immunofluorescence (red) in midbrain tissue sections. (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (Right) Higher-magnification images indicating transduced (EGFP-positive) dopaminergic neurons (TH-positive) with AAV shLuc/EGFP-injected animals (arrowhead: example of a double-positive cell) or AAV shXBP1/EGFP (asterisk: degenerating neurites). (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (B) Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to quantify the extent of neuronal loss after expression of the shXBP1. (Left) Representative images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry followed by Nissl staining. (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (Right) TH-positive neurons were counted and normalized as the percentage of neurons detected on the injected side relative to the noninjected (control) side (n = 3, AAV shXBP1/EGFP; n = 4, AAV shLuc/EGFP). (C) In the same animals as in B, the integrated density of the pixel intensity of images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry covering the entire striatum was calculated to quantify denervation levels (n = 3, AAV shXBP1/EGFP; n = 4, AAV shLuc/EGFP). (D) WT mice were injected with AAVs carrying either shXBP1/EGFP or shLuc/EGFP into the SNpc by brain stereotaxis. (Left) After 2 wk, midbrains were dissected and analyzed by Western blot to monitor ERp72 and calreticulin levels. EGFP levels were also assessed to corroborate the transduction of the SNpc after AAV injections. (Right) Quantification of ERp72 and calreticulin levels relative to TH levels (n = 3 per group). Data are presented as mean and SEM. Statistical analyses were performed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. ns, not significant.