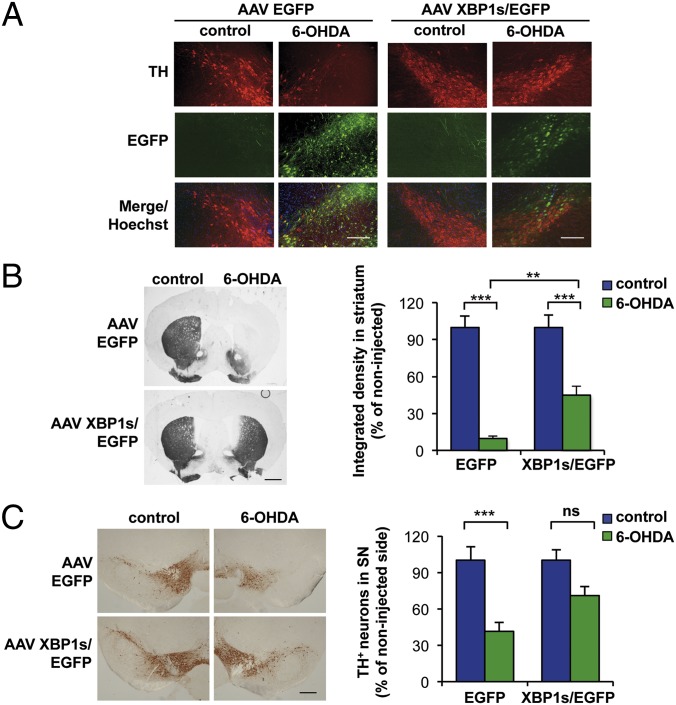
Fig. 4.
Local delivery of XBP1s into the SNpc protects dopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA–induced neurotoxicity. (A) WT animals were injected hemilaterally with AAV carrying either XBP1s/EGFP or EGFP alone into the right SNpc by brain stereotaxis. At 1 mo after AAV delivery, the mice were injected with 6-OHDA into the right striatum. After 7 d, dopaminergic neurons were visualized in midbrain tissue sections by anti-TH immunostaining (red). (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (B) Immunohistochemistry analysis was performed in striatal sections to quantify 6-OHDA–induced denervation in both injected and noninjected sides. (Scale bar: 1 mm.) (Right) The integrated density of pixel intensity was calculated from images of anti-TH immunohistochemistry covering the entire striatum and expressed as percentage of the noninjected (control) sides (n = 8 per group). (C) Anti-TH immunohistochemistry was performed in the SNpc. (Left) Representative images of anti-TH staining in midbrain tissue sections. (Scale bar: 200 μm.) (Right) TH-positive neurons were quantified as the percentage of neurons in the injected side relative to the noninjected (control) side (n = 8 per group). Data are presented as mean and SEM. Statistical analyses were performed with two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. ns, not significant.