Figure 3.
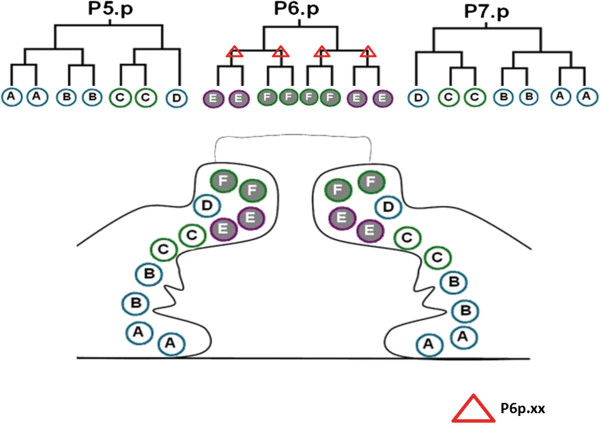
EGL-17/FGF, a known MAPK target shows reduced expression in ndk-1(−) mutant background. The vulva of wild-type hermaphrodites develops from a subset of epidermal blast cells, called vulval precursor cells (VPCs). P(5–7).p VPCs undergo three rounds of cell division and give rise to 22 vulval cells. The vulva at mid-L4 larval stage is composed of 22 cells, which can be grouped into seven cell types (vulA, B1, B2, C, D, E and F). These cells are the great-granddaughters of P5.p-P7.p VPCs (grey filled circles: primary lineages; white circles: secondary lineages). EGL-17/FGF is a known MAPK target, which is expressed in all daughters (P6p.x) and granddaughters (P6p.xx) of P6.p in the L3 stage in wild-type animals. EGL-17/FGF expression was reduced in P6p.xx cells (red triangle) in ndk-1(−) mutants suggesting that Ras/MAPK signaling is inhibited in the absence of NDK-1 [18].