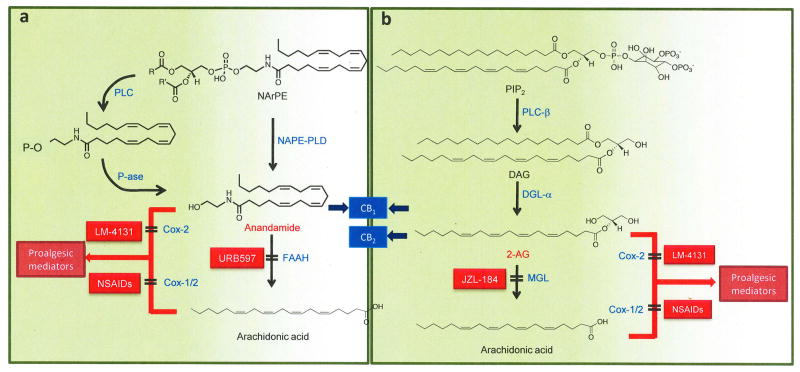
Figure 3. Formation and deactivation of endocannabinoid lipids.
(A) Anandamide is generated by hydrolysis of the membrane lipid, N-arachidonoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (NArPE), which is catalyzed in neurons by a phospholipase D that selectively recognizes N-acylated species of PE (NAPE-PLD). The concentrations of NArPE and anandamide are very low in resting neurons, but quickly increase in response to neural activity and/or neurotransmitter receptor occupation. In macrophages, activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) by the bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide stimulates an as-yet-uncharacterized phospholipase C (PLC), which converts NArPE into phospho-anandamide. This intermediate is dephosphorylated by a phosphatase (P-ase) to form anandamide. Endogenously produced anandamide modulates nociception by binding to CB1 cannabinoid receptors. In both neurons and macrophages, anandamide is converted into arachidonic acid and ethanolamine by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which is selectively blocked by inhibitors such as the O-arylcarbamate derivative, URB597. Anandamide can also be transformed by cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) into proalgesic prostamides, a reaction that is prevented by substrate-selective inhibitors such as LM-4131. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) stop the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins by inhibiting both Cox-1 and Cox-2 activities.
(B) 2-arachidonyl-sn-glycerol (2-AG). Gq-coupled receptors and Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) stimulate phospholipase C-β (PLC-β), which converts phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into 1,2-diacylglycerol (DAG). DAG is hydrolyzed by diacylglycerol lipase-α (DGL-α) to yield 2-AG, which inhibits nociceptive responses by activating CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) terminates 2-AG signaling by hydrolyzing this glycerol ester into arachidonic acid and glycerol. 2-AG and arachidonic acid may be transformed by cyclooxygenase (Cox-1) and/or Cox-2 into various families of proalgesic lipid mediators, which include PGE2 glycerol ester (derived from 2-AG) and PGE2 (derived from arachidonic acid).