FIG. 1.
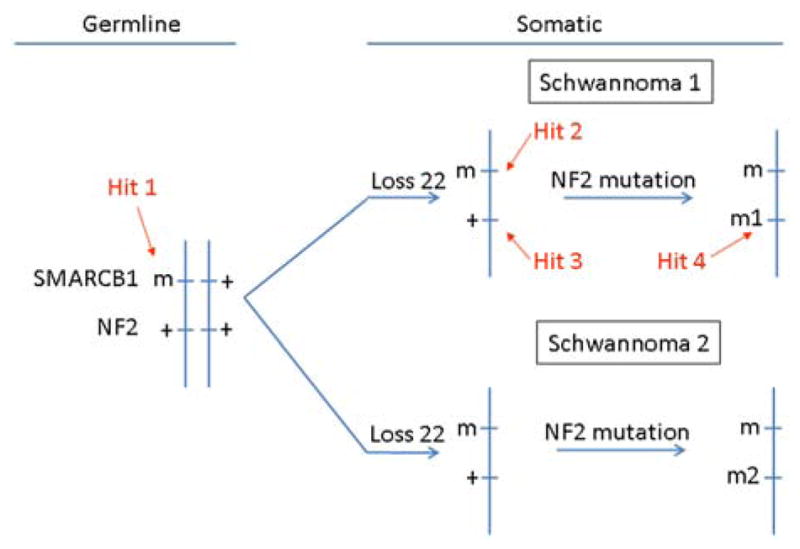
Four-hit, three-step mechanism for SMARCB1 and NF2 inactivation in multiple schwannomas of a SMARCB1-mutation-positive schwannomatosis patient. Tumorigenesis begins with a germline mutation in SMARCB1 (hit 1), and is followed by loss of a portion of chromosome 22 that contains the second SMARCB1 allele and one NF2 allele (hits 2 and 3), and by mutation of the remaining wild-type NF2 allele (hit 4).
