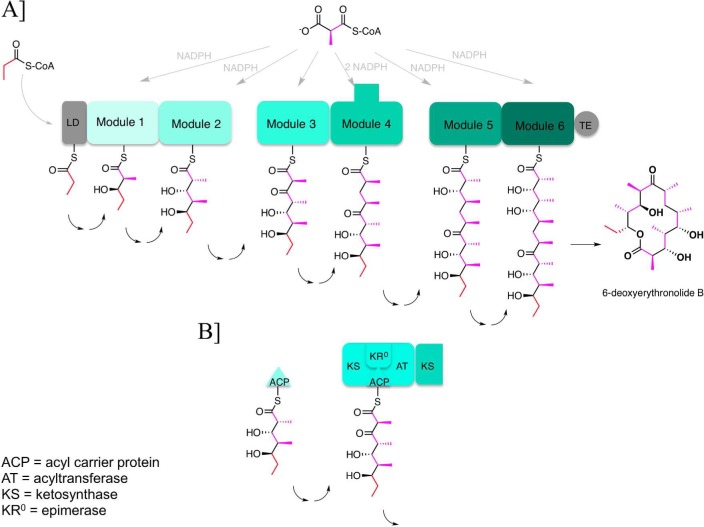
Figure 1.
Assembly line organization of the 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS). (A) DEBS is an ∼2 MDa α2β2γ2 protein assembly that harbors six elongation modules (modules 1–6) flanked by a loading didomain (LD) and a thioesterase (TE). It catalyzes the conversion of 1 equiv of propionyl-CoA and 6 equiv of (2S)-methylmalonyl-CoA into 6-deoxyerythronolide B, using 6 equiv of NADPH as a cofactor. Each module harbors the necessary enzymatic activity for one round of chain elongation and associated modifications of the growing polyketide chain. The reaction intermediates shown attached to the ACP domain of each module correspond to the final products of each of the respective modules. (B) Module 3 is a representative catalytic module within the DEBS assembly line. Its active sites are shown, as is the overall transformation catalyzed by this set of active sites. ACP is the acyl carrier protein, AT acyltransferase, KS ketosynthase, and KR0 a ketoreductase homologue that lacks NADPH-dependent reductase activity but retains epimerase activity.